AI in Healthcare Diagnostics for Transforming Patient Care
Picture a future, happening right now, where diseases are caught earlier and diagnosed with more accuracy than ever before. This is the new reality being built by AI in healthcare diagnostics. These intelligent systems aren’t replacing clinicians; they’re acting as powerful co-pilots.
It’s like giving a seasoned detective a full forensics lab and a team of data analysts, instead of just a magnifying glass.
The New Era of AI in Healthcare Diagnostics
Artificial intelligence is fundamentally changing how medical professionals approach diagnosis. The entire paradigm is shifting from reactive treatment to proactive prediction. By digging through massive datasets: medical images, lab results, patient histories, and more, AI can spot subtle patterns that might be invisible to the human eye. This isn’t just a concept; it’s making a real difference on the clinic floor today.
The momentum is undeniable. The global AI diagnostics market shot up from $1.2 billion in 2023 and is on track to hit $5.4 billion by 2030. This isn’t just about market growth; it’s about real-world adoption. A recent survey found that 66% of physicians are now using AI for tasks like assistive diagnosis; that’s a stunning 78% jump from the previous year. It shows just how much clinicians are coming to rely on these tools to make sense of complex data, faster and more accurately.

From Potential to Practice
Making this leap into a new era takes more than just smart algorithms. It demands a careful mix of technology, solid data governance, and deep clinical expertise. As we step into the new era of AI in healthcare diagnostics, it’s also helpful to understand how broader IT services healthcare solutions fit into the bigger picture of improving patient care.
This guide will walk you through the core ideas and applications that every healthcare leader should know. Right now, AI is already making a huge impact in several key areas:
-
Speeding Up Image Analysis: AI models can analyze X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans in a matter of seconds, flagging potential trouble spots for radiologists to review.
-
Catching Diseases Earlier: By tracking health records over time, AI can predict the onset of conditions like sepsis or diabetic retinopathy long before clear symptoms appear.
-
Creating Personalized Treatment Plans: In oncology, AI helps doctors analyze genomic data to recommend therapies that are specifically designed for a tumor’s unique genetic profile.
This marks a fundamental shift away from one-size-fits-all medicine toward true precision care, where diagnostics and treatments are tailored to each individual. The ultimate goal is to improve patient outcomes by making medical decisions smarter, faster, and more data-driven.
Successfully navigating this change requires a solid grasp of both the clinical and technical sides of the equation. Finding the right AI solutions partner can help organizations build and roll out diagnostic tools that are effective, compliant, and genuinely impactful. In the following sections, we’ll dive deeper into the technologies, real-world examples, and strategic roadmaps shaping the future of medicine.
Understanding the Core AI Diagnostic Engines
To really get a feel for how AI is changing healthcare diagnostics, we need to pop the hood and look at the core technologies making it all happen. These aren’t just buzzwords; they’re powerful engines, each with a specific job in turning raw medical data into something a doctor can actually use. Think of them as a team of highly specialized digital assistants.
At the very center of this is Machine Learning (ML). Picture a medical student poring over thousands of patient files: symptoms, lab results, outcomes. With enough time, that student starts to see patterns and connect the dots. ML does pretty much the same thing, just on a massive scale. It chews through historical data to learn relationships and predict outcomes without someone having to code every single possibility.
Taking that a step further, we have Deep Learning (DL). If ML is the hard-working med student, DL is the world-renowned specialist who’s seen millions of medical images. It uses incredibly complex, multi-layered “neural networks” to pick up on subtle patterns that are often completely invisible to the human eye. This makes it an absolute powerhouse for analyzing medical images.
The Key Players in AI Diagnostics
So, how do these concepts actually show up in the real world? Let’s break down the main engines you’ll find in today’s diagnostic tools. Each has its own unique talent, from “seeing” X-rays to “understanding” a doctor’s notes.
-
Computer Vision (CV): This is the technology that gives a machine “sight.” It’s trained to process and make sense of visual information like X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and pathology slides. By learning from millions of labeled images, a CV model can spot anomalies: tumors, fractures, or the tell-tale signs of diabetic retinopathy, with incredible precision.
-
Natural Language Processing (NLP): A huge amount of a patient’s story is tucked away in unstructured text, like a doctor’s handwritten notes, research papers, or the patient’s own medical history. NLP is the key that unlocks all that information, letting machines “read” and pull out the important details. It can help find the right patients for a clinical trial or even just summarize a long medical record for a quick review.
These engines rarely work in isolation. The most sophisticated AI diagnostic tools actually blend them together. A top-tier system might use Computer Vision to analyze a chest scan while simultaneously using NLP to check the patient’s clinical history for related symptoms, giving a much fuller, more contextual picture.
Putting It All Together
Let’s walk through an example. Imagine an AI workflow for detecting cancer.
A Deep Learning model built for Computer Vision could scan a mammogram and flag a suspicious lesion. At the same time, an NLP model could be scanning that same patient’s electronic health record, looking for risk factors mentioned in a physician’s notes, like “family history of breast cancer.”
This combined approach gives clinicians a 360-degree view, helping them make faster, more confident decisions. As we explored in our guide to implementing healthcare analytics, the real magic happens when you can bring different types of data together. The synergy between these AI engines is what takes diagnostics from simple pattern matching to a truly intelligent support system for doctors.
AI Diagnostics in Action Across Clinical Fields
It’s one thing to talk about AI in the abstract, but seeing it on the clinic floor is where its real power becomes clear. These intelligent tools are already making a tangible difference in AI in healthcare diagnostics, working alongside clinicians to sharpen insights, streamline workflows, and improve patient outcomes. The broader healthcare services industry is feeling this shift, as diagnostic processes get a major upgrade.
This isn’t just a niche technology anymore. We’ve reached a point where nearly 59% of medical practitioners worldwide are using AI for jobs like image analysis and risk prediction. The trust is growing, too. A solid 42.58% of clinicians now have strong confidence in AI-driven recommendations, which is leading to more precise, data-backed treatment plans.
Radiology and Medical Imaging
If there’s one field where AI has become a star player, it’s radiology. Deep learning algorithms are now sifting through X-rays, CT scans, and mammograms with incredible speed and an eye for detail.
Think about it: an AI model can scan a mammogram and flag tiny calcifications that signal early-stage breast cancer, sometimes before they’re even visible to the human eye. The goal isn’t to replace the radiologist. Instead, the AI acts as a tireless second set of eyes, highlighting areas that need a closer look and dramatically cutting the risk of a missed diagnosis. This same idea is being used to spot lung nodules in chest X-rays and pick up on the subtle signs of a stroke in brain scans.
Pathology and Cellular Analysis
Pathology is also getting a major overhaul. For decades, pathologists have manually examined tissue slides under a microscope to grade tumors – a process that’s both time-consuming and can vary from one expert to another.
AI-driven digital pathology tools are changing that game entirely. These systems can scan a whole slide at high resolution, count specific cell types with perfect accuracy, and provide objective, consistent tumor grading. This frees up pathologists to pour their expertise into the most complex and ambiguous cases, making cancer diagnosis more efficient and reliable.
By automating the repetitive, data-heavy tasks, AI lets clinicians focus on what they do best: applying their deep medical knowledge to interpret complex findings and make critical decisions for their patients.
Cardiology and Predictive Analytics
In cardiology, AI’s ability to see into the future is a game-changer. By analyzing ECG data, AI models can spot faint electrical patterns in the heart’s rhythm that predict a future cardiac event, like atrial fibrillation or even sudden cardiac arrest.
These systems can also monitor data from wearable devices around the clock, giving early warnings that allow doctors to intervene before something happens. It’s a huge leap from simply reacting to a cardiac event after the fact.
Oncology and Personalized Medicine
Oncology is where AI’s talent for connecting the dots across massive datasets truly shines. An AI platform can take a patient’s genomic data, tumor characteristics, and clinical history and pull it all together to suggest a personalized treatment plan.
It can match a tumor’s specific genetic mutations with the most effective targeted therapies available. These kinds of real-world success stories, much like some of our own client cases, show the immense value AI is already bringing.
Of course, putting these tools into practice requires a strong foundation. Success hinges on rock-solid healthcare software development that ensures these systems fit neatly into existing workflows and meet all the strict regulatory requirements.
Navigating Implementation and Regulatory Challenges
Adopting AI in healthcare diagnostics isn’t as simple as installing a new piece of software. It’s a journey that demands a realistic look at the real-world obstacles, from messy data to complex legal frameworks. To successfully get these systems off the ground, you have to meet these challenges head-on with a solid plan.
Everything starts and ends with data. High-quality, diverse, and accurately labeled datasets are the fuel for any effective AI model. Without good fuel, even the most powerful engine will sputter and fail, producing unreliable or, worse, dangerously biased results. This means breaking down data silos, cleaning up inconsistent records, and treating every piece of information with the respect it deserves.
A huge part of that respect is following strict privacy laws. Patient data is some of the most sensitive information out there, so compliance isn’t just a good idea; it’s mandatory.
The Bedrock of Trust: HIPAA Compliance
In the United States, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is the law of the land for protecting patient health information. Any AI system that even comes close to this data must be designed from its very foundation with security and privacy in mind.
This goes way beyond basic encryption. It means setting up strict access controls to see who is touching the data and when, keeping detailed audit trails of all activity, and de-identifying data whenever possible during the model training phase. The penalties for non-compliance are severe, but the damage to patient trust can be irreversible. As we explored in our guide to developing HIPAA-compliant applications, navigating these rules is critical.
Confronting Algorithmic Bias
One of the most serious and subtle challenges is algorithmic bias. If an AI model is trained mostly on data from one demographic, its performance can drop dramatically when it sees patients from other groups. This doesn’t just lead to bad medicine; it can reinforce and even worsen existing health disparities.
Imagine an algorithm trained to spot skin cancer almost exclusively on images from light-skinned individuals. That same tool might completely miss a dangerous melanoma on a patient with darker skin.
Mitigating bias isn’t an accident; it requires a deliberate, focused effort to build datasets that truly reflect the entire patient population. This involves actively sourcing diverse data and constantly checking the model’s performance across different demographic groups to make sure the outcomes are fair for everyone.
Weaving Through the Regulatory Maze
Beyond data and bias, AI diagnostic tools have to navigate a complicated web of regulations. In the U.S., most AI-driven medical devices must get clearance or approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This is a rigorous process that requires extensive clinical validation to prove the tool is both safe and effective for its intended purpose.
And it’s not just an American issue; the regulatory environment is evolving worldwide. Frameworks like the EU AI Act are bringing in new rules around transparency, risk management, and the need for human oversight. Staying compliant means keeping a close eye on these shifting regulations and building systems that are flexible enough to adapt.
The market’s potential is undeniable. The global AI in healthcare sector is expected to balloon from $39 billion in 2025 to an incredible $504 billion by 2032. But this growth is held back by governance risks and regulatory hurdles; only 2% of AI systems are currently deployed across entire enterprises. Still, with 31% of organizations already reporting a moderate return on their investment, the momentum is building. You can find more details in these global healthcare industry outlooks on deloitte.com. Clearing these implementation hurdles is the key that will unlock AI’s true potential to improve diagnostics for all.
Your Step-By-Step AI Implementation Roadmap
Jumping from a great idea to a functioning AI tool in a clinical setting is a huge leap. If you try to do it without a clear, structured plan, you’re setting yourself up for failure. Think of it like trying to build a new hospital wing without blueprints; it’s going to be chaotic, expensive, and ultimately, it won’t work.
A phased, deliberate approach is the only way to go. It de-risks the investment, builds crucial trust with your clinicians, and paves the way for a successful rollout.
The first step isn’t about the tech at all. It’s about finding a genuine clinical need. The best AI projects I’ve seen are the ones that zero in on a specific, high-impact problem. Don’t ask, “Where can we stick some AI?” Instead, ask, “What’s our most frustrating diagnostic bottleneck, and could AI be the answer?” Getting that strategic alignment right from the start is the foundation of a strong business case.
Once you have a clear objective, everything shifts to the data. Data is the fuel for any AI system, so getting your data acquisition and governance strategy right is non-negotiable.
Phase 1: Define the Strategy and Scope
This first phase is all about planning. You need to get your clinical, technical, and administrative leaders in the same room to agree on a specific, measurable goal. This is where you pinpoint the exact diagnostic workflow you want to improve.
Key activities here usually involve:
-
Pinpointing the Problem: Get crystal clear on the clinical challenge. Are you trying to cut the turnaround time for preliminary chest X-ray reads? Or maybe improve the detection rate of diabetic retinopathy in rural areas? Be specific.
-
Defining Success: How will you know if you’ve won? Decide on your key metrics upfront. Is it better accuracy, a faster diagnosis, lower costs, or improved patient outcomes?
-
A Reality Check: Take a hard look at your organization’s readiness. Do you actually have access to the data you’ll need? What about the technical infrastructure and clinical expertise to even support the project?
Phase 2: Develop Data and Select Technology
With a solid strategy in hand, it’s time to get your data ready and pick the right tools. This phase gets pretty technical and requires you to think hard about your internal resources versus bringing in outside help.
You’ll need to set up a secure pipeline for collecting, cleaning, and labeling your data. At the same time, you have a big decision to make: build a custom model from scratch or partner with a vendor that offers a pre-validated solution. The right answer depends entirely on your specific needs, budget, and the expertise you have in-house. This is also the point where you must ensure your system will play nicely with your existing EMR/EHR, a common stumbling block we cover in our guide to EHR integration best practices.
Navigating the biggest hurdles: data quality, compliance, and bias, is what this phase is all about.
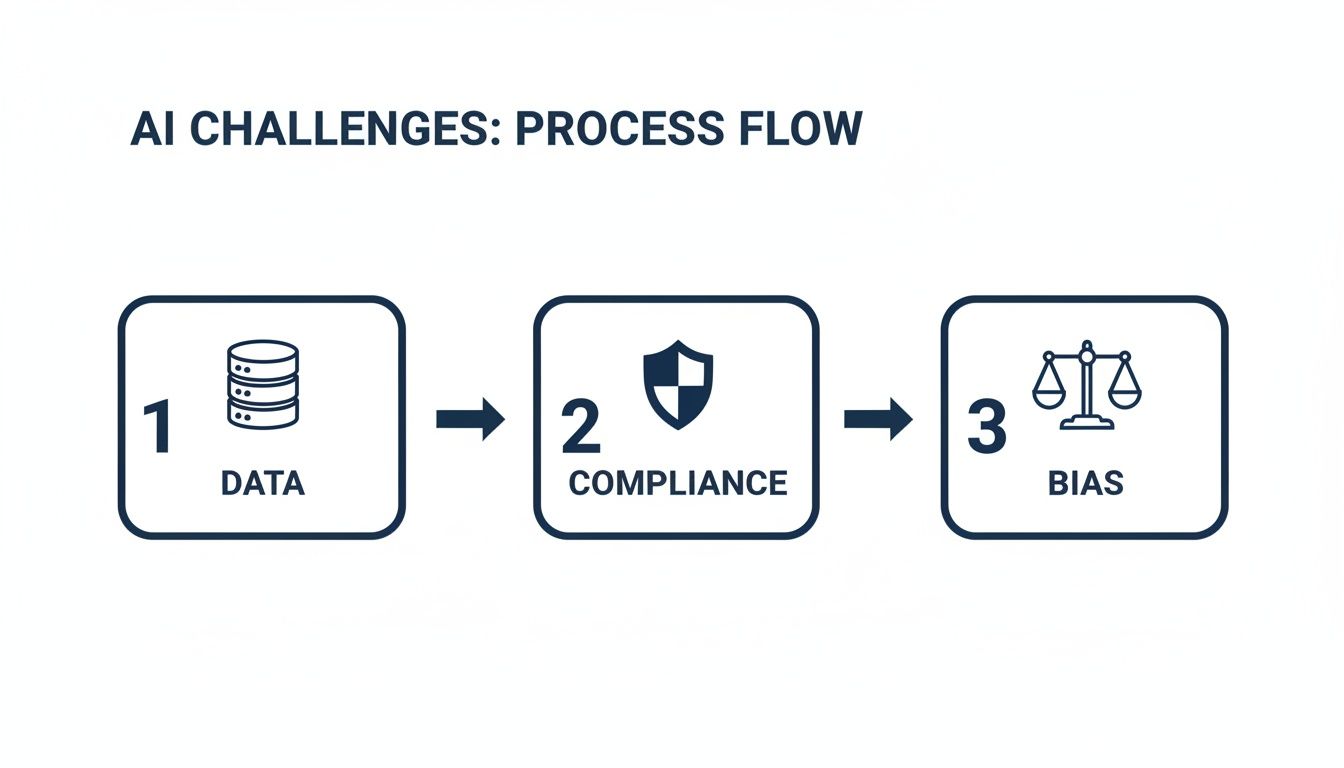
This process highlights the critical hurdles every AI diagnostic project must clear, from sourcing quality data to ensuring regulatory compliance and weeding out algorithmic bias.
Phase 3: Execute a Pilot Program
Never, ever go for a full-scale rollout without a pilot program first. This is your chance to test the AI tool in a controlled, real-world environment. You’ll get to validate its performance and, just as importantly, figure out how to weave it into your existing clinical workflows.
Start small, prove value, then scale. A successful pilot is your best internal marketing tool. It shows tangible benefits to clinicians and administrators, building the momentum you need for wider adoption.
The pilot should run side-by-side with your current process, which gives you a direct, apples-to-apples comparison. It’s absolutely critical to get feedback from the end-users – the clinicians themselves. This will help you find any friction points and make sure the tool is actually helpful, not just another administrative burden. That feedback loop is what turns a good tool into a great one.
Here’s a quick look at how these phases compare, helping you see the journey from a high level.
AI Diagnostic Implementation Phase Comparison
| Implementation Phase | Key Activities | Primary Goal | Key Stakeholders |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Strategy & Scope | Problem identification, ROI analysis, feasibility study, metric definition. | To align on a specific, high-value clinical problem and define success. | Clinical leadership, IT/data science leads, hospital administration, department heads. |
| Phase 2: Data & Tech | Data acquisition & labeling, vendor vs. build analysis, infrastructure setup. | To prepare high-quality data and select the appropriate AI technology. | Data scientists, IT infrastructure teams, compliance officers, potential vendors. |
| Phase 3: Pilot Program | Controlled real-world testing, workflow integration, user feedback collection. | To validate the AI's performance and usability in a clinical setting. | Frontline clinicians (radiologists, pathologists), nurses, IT support, project managers. |
Each phase builds on the last, creating a solid foundation for a tool that not only works technically but is also embraced by the people who use it every day.
Where Diagnostics Is Headed And What to Do Next
Looking ahead, the integration of AI in healthcare diagnostics isn’t just about making existing tools better; it’s about fundamentally changing how we approach patient care. The next wave of innovation won’t just refine algorithms. It will create entirely new ways of seeing the patient as a whole person.
This shift is steering us toward an exciting concept called multimodal AI. Think about it: right now, a system might analyze a chest X-ray in isolation. A multimodal system, on the other hand, could look at that same X-ray while simultaneously pulling in the patient’s genomic profile, lab results, and the doctor’s clinical notes. It weaves these disparate threads together to form a rich, multidimensional picture of a person’s health, uncovering insights that are impossible to spot when viewing each data point on its own.
Making Way for Hyper-Personalized Medicine
Another fascinating area to watch is generative AI. Beyond its more publicized uses, it has a critical role to play in creating high-quality synthetic data. This is a game-changer for training more robust and fair AI models, particularly for rare diseases where real-world data is incredibly scarce – a common roadblock we pointed out in our guide on selecting AI use cases for your business.
All these advancements point toward a single, powerful destination: hyper-personalized medicine. This is the future we’re building, one where diagnostic insights translate directly into treatments crafted for an individual’s unique biological and genetic signature.
The journey into AI-powered diagnostics isn’t just about adopting new technology. It’s about fundamentally raising the standard of care and building a more proactive, predictive, and personalized healthcare system for everyone.
Stepping into this future requires both a clear vision and the right team. Turning this potential into a clinical reality often means partnering with an experienced AI solutions partner who gets both the technology and the very specific demands of the healthcare world. By taking smart, strategic steps today, your organization can find itself at the leading edge of this medical evolution.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI in Diagnostics
What is the biggest challenge of implementing AI in healthcare diagnostics?
The single biggest hurdle is data. Accessing high-quality, diverse, and accurately labeled datasets is crucial, as healthcare data is often siloed, inconsistent, and protected by strict privacy regulations like HIPAA. Building a solid data foundation is the most critical first step for any reliable AI diagnostic tool.
How is the safety and efficacy of an AI diagnostic tool ensured?
Ensuring safety is a multi-step process. It starts with rigorous clinical validation to prove the tool’s accuracy against established standards. Next, it must receive regulatory clearance from bodies like the FDA, which requires extensive evidence of safety and effectiveness. Finally, continuous real-world monitoring with clinician oversight provides the ultimate safety net.
Will AI replace doctors in the diagnostic process?
No, the goal of AI in healthcare diagnostics is to augment, not replace, clinicians. AI acts as a powerful co-pilot, analyzing vast amounts of data to identify patterns and provide insights. However, it lacks the empathy, holistic judgment, and nuanced experience of a human doctor, who makes the final, informed clinical decision.
How can a smaller hospital or clinic get started with AI diagnostics?
Smaller organizations can start by focusing on a single, high-impact problem, such as automating the preliminary analysis of a common imaging test. Partnering with a vendor offering specialized AI development services is often more effective than building a system from scratch. A small, successful pilot project can prove value and build momentum for wider adoption.
Ready to explore how AI for your business can elevate your diagnostic capabilities? At Bridge Global, we specialize in building secure, compliant, and impactful AI solutions for the healthcare industry. Our expertise in custom software development and deep focus on healthcare software development make us the ideal AI solutions partner to guide your journey from concept to clinical reality.



