Software Engineering in Healthcare Explained
When we talk about software engineering in healthcare, we’re not just talking about digitizing paper records. We’re talking about building the very systems that improve how doctors treat patients, how clinics operate, and how medical data flows securely from one point to another. It’s a unique field that blends sophisticated technology with the unforgiving realities of medical regulations and patient safety.
This means creating everything from AI-powered diagnostic tools that spot subtle patterns in medical scans to secure telehealth platforms that bring a specialist’s expertise into a patient’s living room. It’s a high-stakes environment where engineering precision directly impacts human lives. Check out some of our client cases to know the AI-powered diagnostic tools and healthcare software that we’ve built.
The New Heartbeat of Modern Medicine

Think of software as the new central nervous system of the entire healthcare industry. It’s no longer a background utility; it’s the connective tissue linking patient data, life-saving medical devices, and clinical decision-making. The old world of isolated, paper-stuffed folders is giving way to an interconnected digital environment.
This isn’t just an upgrade—it’s a complete reimagining of how healthcare works. We’re shifting from static, historical records to dynamic, intelligent systems that can actively help improve patient outcomes.
Where Software Is Making a Real-World Impact
The applications aren’t just theoretical. They are practical tools solving real, everyday challenges in clinics and hospitals right now.
-
Telehealth Platforms: These platforms have become a lifeline, connecting patients in remote areas or those with mobility issues to specialists located hundreds of miles away. It completely removes geography as a barrier to care.
-
AI-Powered Diagnostics: Machine learning models are being trained to analyze X-rays, MRIs, and other medical images, often spotting anomalies the human eye might miss, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses.
-
Electronic Health Records (EHRs): A modern EHR is far more than a digital filing cabinet. It gives clinicians a single, unified view of a patient’s entire medical history in real-time, which is crucial for making fast, informed decisions.
-
IoT Wearables: Smartwatches and other home monitoring devices track vital signs and can automatically alert a care team to a potential problem before it escalates into a full-blown emergency.
At its core, this shift is about building a smarter, more accessible, and deeply personalized healthcare system. The technology isn’t just for efficiency’s sake—it’s a direct contributor to patient safety and better health outcomes.
This guide is your roadmap to building these critical systems. We’ll walk through everything from navigating the maze of regulations like HIPAA to making data truly interoperable with standards like FHIR. We’ll also get into the practical side of applying AI and IoT to create software that meets the industry’s toughest demands. You can see how we put these principles into practice by exploring our work in healthcare software development.
Building on a Foundation of Trust

In healthcare, software isn’t just about a slick interface or fast performance. It’s about protecting lives and handling some of the most sensitive data imaginable. While functionality matters, trust is the non-negotiable foundation.
Before your team even thinks about features, any project in this space must be grounded in three core principles: compliance, security, and interoperability. Cutting corners here isn’t a technical debt; it’s a critical failure that can lead to massive fines, a shattered reputation, and, worst of all, patient harm. These aren’t just checkboxes—they must be woven into the very fabric of your design from day one.
Compliance: The Blueprint for Building Trust
When engineers hear “HIPAA,” their minds often jump to a long list of constraints. But it’s better to think of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) as a blueprint for building trust, not a rulebook of what you can’t do. It guides you on how to thoughtfully and ethically handle Protected Health Information (PHI).
Adopting a “compliance-first” mindset means that every decision, from how you structure a database to the way you authenticate users, is made with patient privacy as the top priority. This proactive stance transforms regulatory hurdles into guardrails, steering you toward building software that is both responsible and reliable.
Security: The Digital Immune System
A hospital has guards and locked doors. Its digital infrastructure needs an equally robust immune system. In today’s threat environment, a simple firewall just doesn’t cut it anymore. Cybersecurity in healthcare requires a multi-layered defense strategy to fend off a relentless stream of attacks.
The stakes are astronomically high. In 2023 alone, a staggering 112 million people had their private health data exposed by over 540 organizations. This reality underscores just how critical advanced security is for any healthcare software project. To learn more about this evolving landscape, check out our full guide to custom healthcare software development.
A truly comprehensive approach includes:
-
End-to-End Encryption: Data has to be locked down whether it’s moving across a network (in transit) or sitting in a database (at rest). If bad actors intercept it, the information remains unreadable garbage.
-
Proactive Threat Modeling: This is about thinking like an attacker. Your team needs to hunt for potential weaknesses in the application’s design before they can be exploited, not just react to a breach after the damage is done.
-
Strict Access Controls: A receptionist doesn’t need access to a patient’s entire surgical history. Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures users can only see and touch the specific information they need to do their jobs.
Security isn’t a one-and-done setup. It’s a constant process of vigilance, adaptation, and improvement. In healthcare, it’s a direct component of patient safety.
Interoperability: The Universal Translator
Imagine a world where a doctor in one hospital couldn’t read the notes from a specialist across town because they spoke different languages. For a long time, that’s exactly what healthcare data felt like—a collection of isolated islands. Interoperability is the universal translator that finally connects them.
This is where data standards come into play. They provide a common language and structure for exchanging clinical and administrative information, allowing different systems to communicate seamlessly.
The table below outlines some of the most critical standards your engineering team needs to master.
Key Healthcare Regulatory and Interoperability Standards
| Standard/Regulation | Primary Focus | Key Development Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| HIPAA | Patient data privacy and security | Implement strict access controls, encryption, and audit trails for all PHI. |
| GDPR | Data protection for EU citizens | If your software serves EU residents, you must ensure data portability and the “right to be forgotten.” |
| HL7 v2 | Clinical data messaging | The workhorse standard for exchanging data between systems like EHRs and labs. It’s event-driven and widely adopted. |
| FHIR | Modern, API-based data exchange | A flexible, web-based standard for accessing discrete data elements. Essential for mobile apps and modern integrations. |
| DICOM | Medical imaging | The global standard for transmitting, storing, and viewing medical images like X-rays and MRIs. |
Building with these standards in mind means your application can both “speak” and “listen” in the language of healthcare. When an EHR, a lab system, and a pharmacy tool can all share data effortlessly, you create a cohesive, unified view of the patient. The result? Better-coordinated care, fewer medical errors, and dramatically improved outcomes.
Architecting Systems Built for the Future

How do you build a healthcare application that won’t become obsolete in five years? The secret is in the architecture—the foundational blueprint that dictates how a system is organized, how its pieces talk to each other, and how it can evolve. The architectural choices you make today will directly define your system’s future performance, security, and ability to keep up with new medical breakthroughs.
Picking the right structure is a bit like deciding whether to build a single, massive skyscraper or a campus of interconnected buildings. Each approach has its merits, and the best choice depends entirely on what the healthcare solution needs to accomplish. Building on a solid architectural foundation is a core principle of our entire approach to custom software development.
Monolithic vs. Microservices Architectures
In the world of software architecture, two patterns stand out: monolithic and microservices. For any leader or developer steering a healthtech project, getting a handle on their trade-offs is essential.
-
Monolithic Architecture: Imagine this as an all-in-one hospital management system. Every function—patient registration, billing, scheduling, pharmacy—is woven into a single, unified application. It’s often simpler to get off the ground because everything lives in one codebase. But that simplicity has a downside. A small bug in the billing module could crash the entire system. Updating a single feature means re-deploying the whole application, making it rigid and slow to adapt.
-
Microservices Architecture: This approach carves up that same hospital system into a collection of small, independent services. Patient registration is one service, billing is another, and scheduling is a third. Each one can be developed, updated, and scaled on its own. If the scheduling service gets hammered with traffic, you can give it more resources without touching anything else. This modularity offers incredible flexibility and resilience—critical traits in the ever-changing healthcare field.
While microservices provide fantastic long-term scalability and agility, their complexity isn’t always justified. A monolithic build might be the perfect fit for a smaller, specialized clinical tool with a very clear, defined scope.
The Role of Cloud Services and Data Design
Modern healthcare applications are data factories, constantly generating and consuming everything from high-resolution medical scans to real-time feeds from IoT monitors. This is where cloud services become non-negotiable. They offer the on-demand power and reliability needed for mission-critical systems like EHRs and telehealth platforms, providing the elasticity to handle fluctuating patient loads and the robust infrastructure to ensure constant availability.
Just as critical is the design of your databases. A thoughtfully structured database is the key to managing enormous volumes of sensitive patient data securely and efficiently. This means paying close attention to:
-
Schema Design: Carefully planning how data is organized to guarantee fast queries and maintain data integrity.
-
Data Encryption: Protecting patient information both at rest (while stored in the database) and in transit (as it moves across the network).
-
Scalability Planning: Engineering the database to grow gracefully as years of patient data pile up.
Finally, effective API (Application Programming Interface) design is the glue holding it all together. APIs are the communication channels that let different software components—like an EHR talking to a lab information system—exchange information seamlessly. A well-designed API is secure, reliable, and clearly documented, ensuring that new features and third-party tools can be plugged in without breaking existing workflows. These are the architectural cornerstones of any truly sustainable solution in healthcare software.
4. How AI and IoT Are Fundamentally Changing Patient Care
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) aren’t just buzzwords anymore; they’re real-world tools that are actively reshaping how patient care is delivered. The core of modern software engineering in healthcare is figuring out how to weave these technologies together to build systems that are more proactive, personalized, and predictive. We’re finally moving away from simply reacting to illness and toward preventing it in the first place.
Think of an AI algorithm as a brilliant specialist who works 24/7. It can sift through thousands of MRIs or CT scans, spotting tiny anomalies that a human radiologist might miss, flagging potential diseases at their earliest stages. This isn’t about replacing clinicians. It’s about giving them a powerful co-pilot to augment their diagnostic skills.
Meanwhile, IoT devices are the sentinels on the ground. Smartwatches, continuous glucose monitors, and even smart beds are constantly collecting real-time health data, right from a patient’s home. This steady stream of information paints a far more complete picture of a person’s health than the occasional 15-minute office visit ever could.
Turning Raw Data into Actionable Insights
The real breakthrough happens when AI and IoT join forces. IoT devices collect the data, and AI gives it meaning.
-
Managing Chronic Conditions: An IoT-enabled blood pressure cuff tracks a patient’s readings at home. If the numbers start creeping up, an AI system can spot the trend, check it against the patient’s medical history, and flag the care team for an early intervention—long before it becomes a crisis.
-
Keeping an Eye on Post-Op Recovery: After surgery, wearable sensors can monitor a patient’s heart rate, oxygen levels, and how much they’re moving. This allows for safe remote monitoring, which can shorten hospital stays while catching early signs of complications like infections or blood clots.
-
Making Hospitals Run Smoother: Inside a hospital, IoT sensors can track the location of vital equipment like ventilators or infusion pumps. AI can then analyze usage patterns to optimize where this equipment is placed, cutting down on the time nurses waste searching for what they need.
The ultimate goal is a seamless loop: patient data flows from home or the hospital to an intelligent system, which then delivers clear, actionable insights right back to the clinicians. This is precisely where a skilled AI solutions partner becomes invaluable—they can build the complex infrastructure needed to connect all those dots.
How Generative AI Is Lightening the Load
AI’s impact goes far beyond just crunching numbers. Generative AI is now stepping in to handle the mountain of administrative work that burns out clinicians. For instance, AI can now listen in on a doctor-patient conversation and automatically draft a structured summary note for the electronic health record. This simple function can save a doctor hours of documentation every single day.
The global healthcare software market is growing at an incredible pace, projected to hit nearly $981.5 billion by 2032. This explosion is fueled almost entirely by the adoption of AI and machine learning. As we explored in our AI adoption guide, organizations that learn how to put AI for your business to work will lead the next wave of innovation.
Of course, as AI and IoT become more central to patient care, it’s critical to follow the best practices for testing AI models and systems. We have to ensure these tools are safe, reliable, and fair. Building trust in the technology is just as important as building the technology itself.
Bringing these advanced systems to life requires a very specific skill set. We see it every day—when you combine expert IoT software development services with top-tier AI development services, you unlock efficiencies and improve patient outcomes in ways that were impossible just a few years ago. Our work on a remote patient monitoring system is a perfect example of this in action. You can see how we developed a compliant IoT application for a healthcare client and the impact it had.
In the end, this is what software engineering in healthcare is all about: building systems that let doctors be doctors and nurses be nurses. By letting the technology handle the data, we free up clinicians to focus on what truly matters—caring for people.
Your Roadmap from Concept to Clinic
Turning a great idea into a healthcare product that gets adopted by clinicians and meets strict compliance standards is a serious undertaking. The initial concept is just the spark; the real work is navigating the complex journey from that idea to a tool that actually works in a clinical setting.
This roadmap breaks down that journey into practical, manageable phases, covering everything from initial discovery and agile development to the rigorous testing and ongoing support that follows.
For a concrete sense of what this looks like, digging into real-world examples like healthcare appointment app development can offer some valuable lessons. A disciplined process is what separates a tool that solves real problems from one that just addresses perceived ones. As a seasoned AI solutions partner, we’ve guided countless organizations through every step.
Phase 1: The Discovery and Strategy Phase
Before a single line of code gets written, you have to do your homework. This is the Discovery phase, and it’s arguably the most important. It’s all about deeply understanding the problem you want to solve by talking to the people on the front lines—doctors, nurses, administrators, and even patients—to get a clear picture of their daily workflows, biggest frustrations, and unmet needs.
The goal here is to set clear, measurable objectives. What does success actually look like? Are you trying to reduce patient wait times by 15%? Or maybe hit an 80% clinician adoption rate within six months? This phase ends with a detailed project blueprint that maps out technical requirements, compliance needs, and a user-focused design strategy.
Phase 2: Agile Development and Clinical Collaboration
With a solid plan in hand, it’s time to start building. We use an agile development approach, but it needs to be tailored specifically for the demands of healthcare. The work is broken down into short, iterative cycles called “sprints,” where cross-functional teams build and test small, digestible pieces of the software.
Here’s the critical part: clinicians have to be involved in every single sprint. Their feedback isn’t something you collect at the end; it’s a core part of the development loop. This constant back-and-forth ensures the final product is intuitive and slots neatly into existing clinical workflows. It’s how you avoid the common trap of building something that’s technically brilliant but practically useless.
The infographic below shows a common workflow where data from wearables is fed to an AI, which then alerts medical staff—a perfect example of modern healthcare software development.
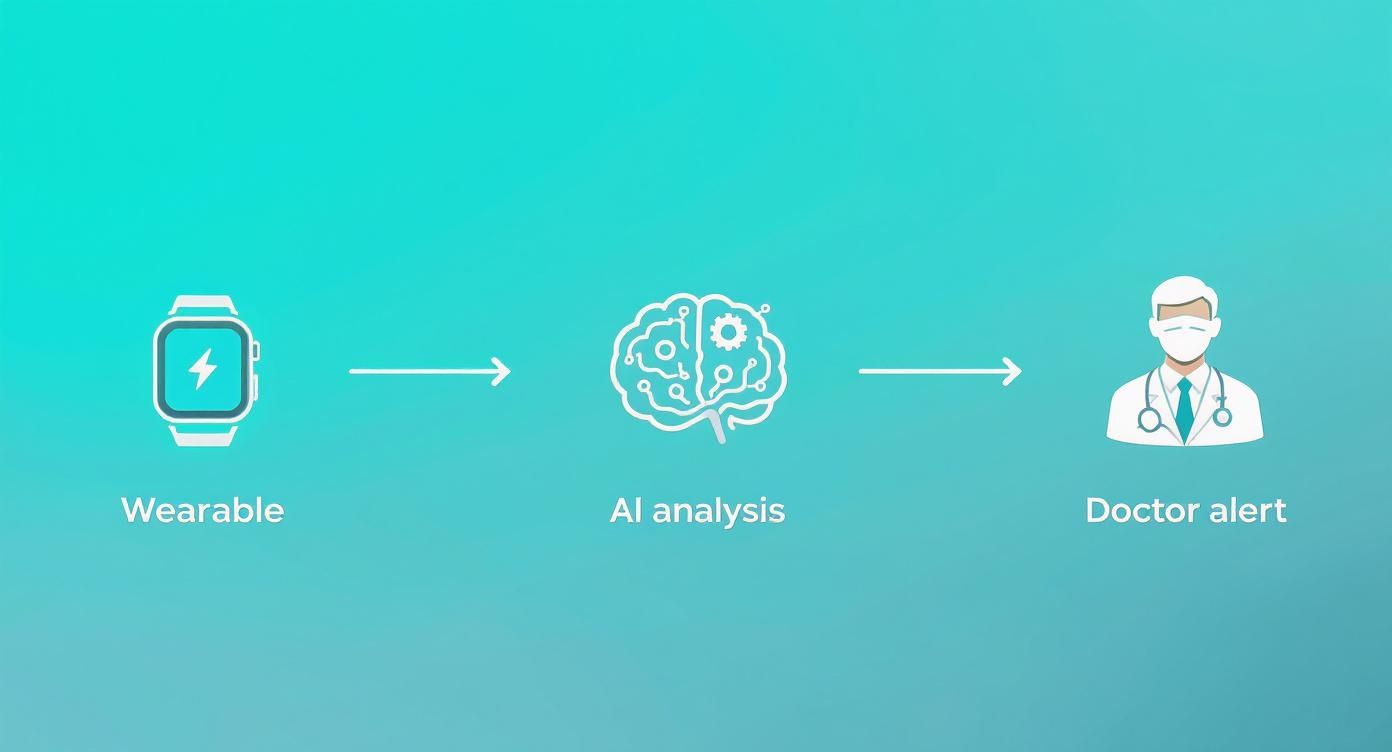
This visual really captures how integrating smart devices and AI can create a proactive care model, turning raw data into alerts that can save lives.
Phase 3: Rigorous Testing and Validation
In healthcare, testing is so much more than just finding bugs. It’s a meticulous, multi-layered process designed to guarantee patient safety, protect data, and ensure the system is completely reliable.
There are several layers of testing that are simply non-negotiable:
-
Integration Testing: Does your software play nice with others? This step confirms it can communicate flawlessly with essential systems like EHRs and lab information systems, which is key for interoperability.
-
Security Testing: We bring in the experts to perform penetration testing and vulnerability scans. The goal is to find and patch any weakness that could expose sensitive patient data.
-
Usability Testing: Real clinicians test-drive the software in simulated environments. This helps us make sure the interface is intuitive and efficient, which dramatically reduces the risk of user error.
-
Compliance Audits: The entire system is put under the microscope and checked against HIPAA and other regulations to ensure every single technical and administrative safeguard is locked down.
Phase 4: Deployment and Continuous Improvement
Getting the software launched isn’t the finish line—it’s the starting line for its life in the real world. After deployment, the focus immediately shifts to monitoring, maintenance, and making it better over time.
This ongoing work includes:
-
Performance Monitoring: Keeping a close eye on key performance indicators (KPIs) like system uptime, response times, and how much the tool is actually being used.
-
User Feedback Collection: Creating easy ways for clinicians to report issues and suggest improvements. Their insights are gold.
-
Regular Updates: Rolling out updates periodically to add new features, patch any security vulnerabilities, and adapt to changing clinical needs and regulations.
A successful roadmap treats healthcare software not as a one-and-done project, but as a living product that evolves. This structured yet flexible approach is what turns an ambitious vision into a compliant, adopted, and truly impactful clinical tool.
Measuring What Truly Matters in Healthtech
When your new healthtech software goes live, that’s just the beginning. In healthcare, success isn’t about download counts or user sign-ups; it’s measured by real-world improvements—better clinical outcomes and smoother operations. We have to look past the vanity metrics to see if the technology is actually making a difference.
This means tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that connect directly to patient care and provider workloads. Forget about generic engagement metrics for a moment and ask the tough questions. Did our system actually reduce patient readmission rates by 15%? Are nurses spending less time on paperwork and more time with patients? What’s the real adoption rate among clinicians, and what are they really saying about it?
From Data to Actionable Insights
Just having the data isn’t enough. The magic happens when you can turn those raw numbers into a clear story about your product’s impact. This is where solid business intelligence services come into play, giving you the power to dig into complex information, prove your ROI, and make smarter decisions for your product’s future.
When you have the right analytics, you can see exactly which features are hitting the mark and where users are getting stuck. It takes the guesswork out of product development.
Think of your software as a living tool that needs to adapt constantly. Continuous improvement isn’t just a nice idea; it’s a core requirement for staying relevant and effective in the fast-paced world of healthcare.
A Framework for Continuous Improvement
A truly successful healthtech product is never “done.” It thrives on a constant cycle of feedback, analysis, and refinement. This loop ensures your software keeps delivering value year after year.
-
Gather Quantitative Data: Use your analytics to watch the critical clinical and operational KPIs. Are diagnostic turnaround times getting shorter? Is medication adherence improving?
-
Collect Qualitative Feedback: Get out there and talk to the people using your software. The firsthand experiences of clinicians and staff provide the “why” behind the data.
-
Analyze and Prioritize: Combine the hard data with the human feedback to figure out where you can make the biggest impact. Maybe a workflow needs a tweak, or a new integration would be a game-changer.
-
Iterate and Redeploy: Roll out the changes in your next development sprint, and then immediately start measuring again.
Building this feedback loop right into your strategy is what separates good healthcare software from great. It’s how you create a tool that genuinely supports providers and patients over the long haul. To see how we’ve put this into practice, check out the measurable results we’ve achieved in our client cases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the biggest hurdles in healthcare software development?
The primary challenges are navigating complex regulatory landscapes like HIPAA and GDPR, ensuring ironclad data security for sensitive patient information, and achieving interoperability so new software can communicate with existing hospital IT systems. Additionally, designing a user experience that busy clinicians will actually adopt is a critical, make-or-break factor.
Can you really use agile in a heavily regulated field like healthcare?
Absolutely, but it requires a “compliance by design” approach. This means integrating regulatory and security requirements into the development process from the very beginning, making them part of every sprint. Constant collaboration between developers, compliance experts, and clinical users ensures that each iteration is compliant, safe, and effective without slowing down the agile workflow.
What is the role of AI in modern healthcare software?
AI acts as a powerful analytical engine. It can help in diagnostics by identifying patterns in medical images that the human eye might miss, predict patient risk factors based on their health records, personalize treatment plans, and automate administrative tasks like clinical documentation. The goal is to augment clinicians’ abilities, allowing them to make faster, more informed decisions and spend more time on patient care. Read more about how healthcare automation redefines workflows & patient care.
How do you ensure the security of a new healthcare application?
Security in healthcare software requires a multi-layered strategy. This includes end-to-end data encryption (both in transit and at rest), strict role-based access controls to limit data exposure, proactive threat modeling to identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited, and regular, rigorous security audits and penetration testing.
We want to build something custom. Where do we even start?
The most important step happens before a single line of code is written: a comprehensive discovery phase. This is where we get crystal clear on the exact problem you’re trying to solve. What does success look like, and how will we measure it? What do the current clinical and operational workflows look like on the ground? It’s vital to bring clinicians, administrators, and IT staff to the table to ensure the requirements are grounded in reality and aligned with your business goals.
Ready to build the future of healthcare technology? At Bridge Global, we combine deep industry expertise with cutting-edge AI to deliver secure, compliant, and impactful software solutions. Contact us now to turn your vision into a clinical reality.



