Augmented Reality in Health Care Explained
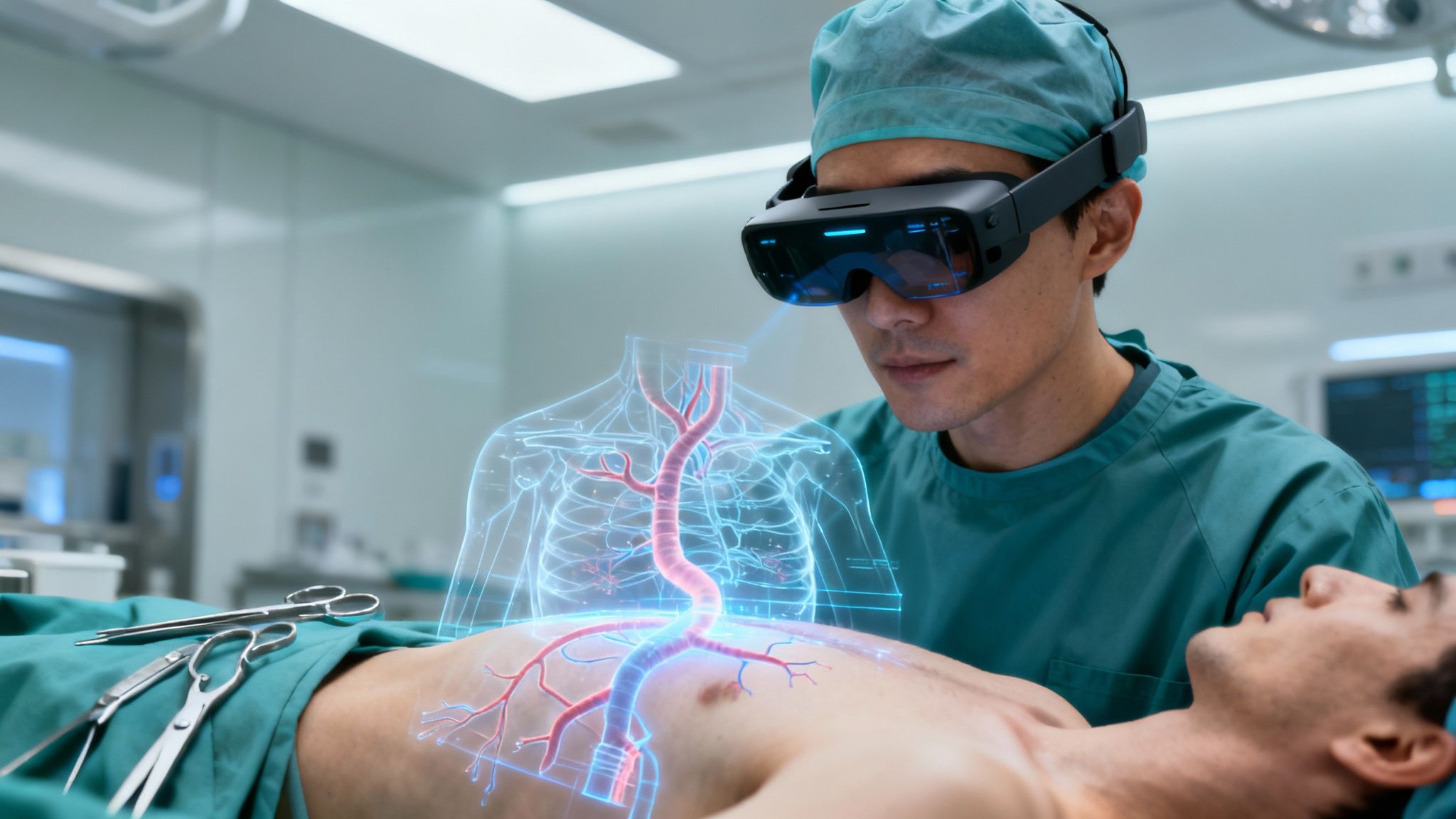
Picture this: a surgeon is in the middle of a complex operation. Instead of glancing back and forth at a monitor, they see a detailed 3D map of the patient’s veins and arteries projected directly onto the patient’s body. Every incision becomes more precise, every action safer. This isn’t a scene from a sci-fi movie; it’s a real-world example of augmented reality in health care.
The New Reality in Modern Medicine
It’s easy to confuse augmented reality with virtual reality, but they’re quite different. VR plunges you into a completely digital world, shutting out your physical surroundings. AR, on the other hand, keeps you grounded in reality and simply adds layers of useful digital information on top of what you already see.
Think of it as an intelligent, transparent guide for medical professionals. This technology is already making a tangible difference in patient outcomes, overhauling medical training, and bringing a new level of precision to surgery. We’re moving past the theoretical and into the practical, where AR is becoming an essential tool in everything from the operating room to the classroom.
The numbers back this up. The global healthcare AR and VR market was valued at $3.4 billion in 2024 and is expected to explode to over $18 billion by 2034. That’s not just growth; it’s a clear signal of widespread adoption.
Why AR Is a Game-Changer
The real magic of AR is its ability to deliver the right visual information exactly when and where it’s needed most. A surgeon no longer has to look away from the patient to check MRI scans or vitals on a screen. That critical data can be projected right into their field of view.
This fundamental shift brings some powerful advantages:
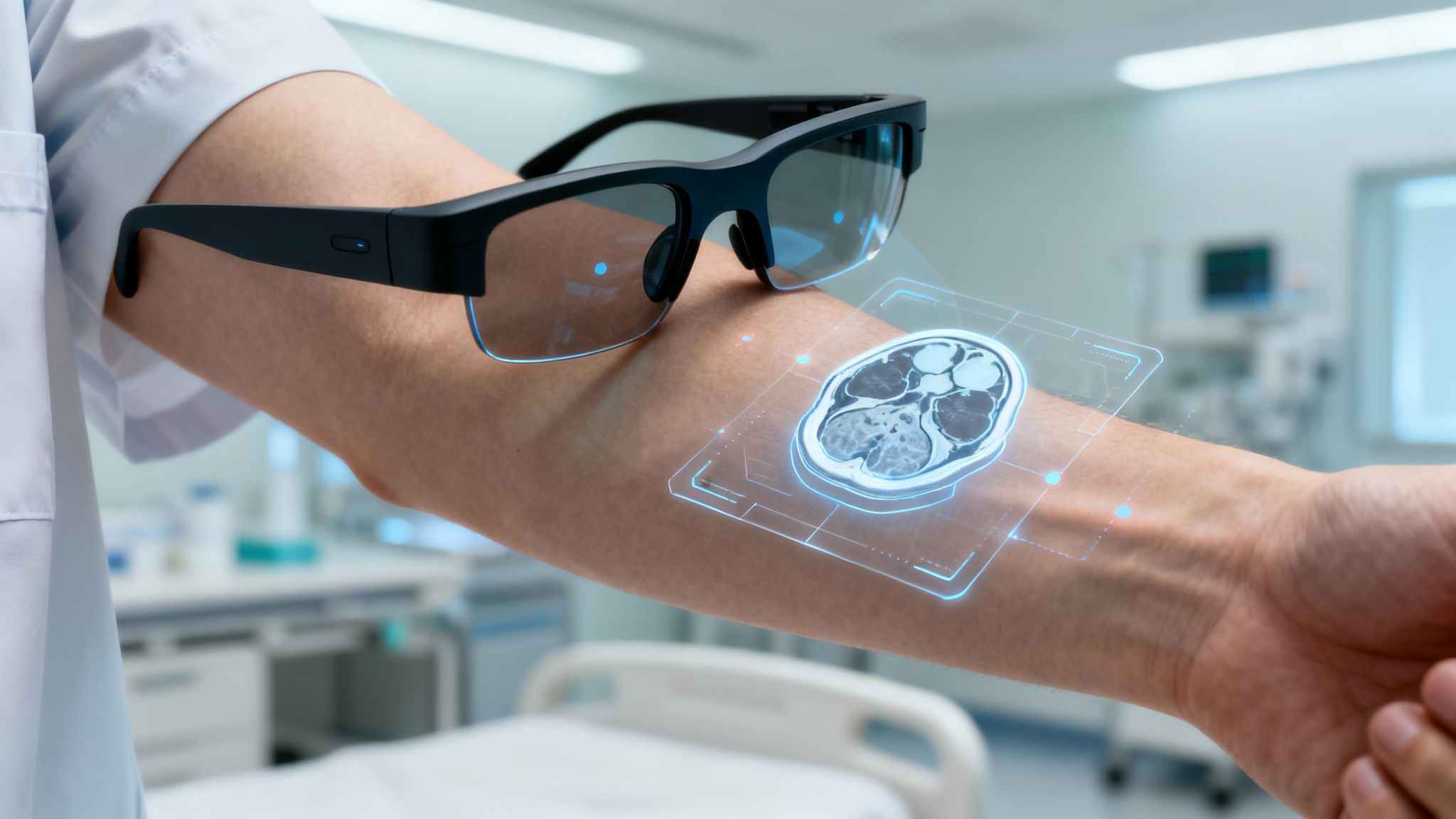
- Enhanced Visualization: AR transforms flat, 2D medical images like CT scans into interactive 3D models. Doctors can walk around them, resize them, and view them from any angle to get a much better understanding of the patient’s anatomy.
- Improved Accuracy: By overlaying digital guides directly onto a patient, AR helps clinicians perform procedures with pinpoint precision. This dramatically reduces the risk of human error during delicate tasks like biopsies or injections.
- Accelerated Learning: Imagine medical students interacting with a dynamic, holographic heart instead of just reading about it in a textbook. AR makes complex biological systems easier to grasp and remember.
Of course, turning this potential into a practical, life-saving reality requires serious expertise. Building effective and compliant tools means partnering with specialists who understand the unique demands of healthcare software development to ensure new solutions work seamlessly in a clinical setting.
How AR Technology Works in a Clinical Setting
So, how does augmented reality actually come to life inside a busy hospital or clinic? It’s less about science fiction and more about creating a transparent, digital layer of information over the real world. Think of it as giving medical professionals a form of X-ray vision.
At its core, the system is a powerful marriage of specialized hardware, like smart glasses or advanced displays, and incredibly sophisticated software. It all starts with familiar medical imaging data, like CT or MRI scans. The system takes this flat, 2D information and converts it into interactive 3D models.
This is where the real magic happens. These digital models are then precisely projected onto the real-world view, whether that’s directly over a patient’s body in the operating room or onto a training mannequin in a classroom.
The Core Components of Medical AR
For this digital overlay to be of any real use, it has to line up perfectly with the physical world. Two crucial processes make this happen: registration and tracking.
Registration is the initial step that makes sure the 3D model aligns exactly with the patient’s real anatomy. Tracking is what keeps it locked in place, even as the patient breathes or the surgeon moves around.
This seamless alignment is what allows a surgeon to “see through” skin to pinpoint a tumor or visualize a complex network of veins with stunning accuracy. Pulling this off requires deep expertise; it’s why many hospitals partner with a custom software development firm to ensure all these intricate parts work together without a hitch.
To get a clearer picture of how these systems are built, let’s break down the essential components that make AR tick in a medical environment.
Key AR Components in Healthcare
| Component Type | Example | Function in Healthcare |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | Smart Glasses (e.g., HoloLens) | Projects digital images directly into the user’s field of view, enabling hands-free interaction during procedures. |
| Software | Medical Imaging Processors | Converts 2D scans (MRI, CT) into interactive, manipulable 3D anatomical models for visualization. |
| Sensors | Cameras & Depth Sensors | Capture the physical environment in real-time to accurately place and track digital overlays. |
| Display | High-Resolution Monitors | Provides a large, shared view of the AR-enhanced scene for surgical teams or educational groups. |
Each piece of the puzzle, from the camera capturing the room to the software rendering the model, has to work in perfect sync to create a reliable clinical tool.
From Data to Real-Time Visualization
The entire process begins long before a surgeon ever puts on a headset. First, the patient’s data is collected and processed. Powerful algorithms then get to work, constructing the 3D models that will act as the digital guide.
Once in the procedure, the AR system uses its sensors to map the room and identify the patient, anchoring the 3D model to specific anatomical landmarks.
This creates a live, dynamic map that updates in milliseconds. If the surgeon turns their head or the patient shifts even slightly, the digital overlay adjusts instantly to maintain that perfect alignment. This real-time feedback loop is what makes AR a critical clinical tool, not just a neat gimmick.
The massive investment flowing into this area tells the story.
Globally, the augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) market in healthcare was valued at approximately USD 3.4 billion in 2024 and is projected to skyrocket to about USD 18.38 billion by 2034. This reflects an impressive compound annual growth rate of 18.38%. Read the full research about the AR/VR healthcare market.
This explosive growth is happening for a simple reason: the technology gives clinicians insights they’ve never had before. Building and implementing these systems require a strong foundation in data management, often supported by robust cloud services to handle the enormous imaging files. As a leading AI solutions partner, we see firsthand how integrating these technologies is no longer a conversation about the future—it’s happening right now.
Real-World Applications of AR in Healthcare
Let’s move from theory to practice. It’s one thing to talk about the technology, but the real-world applications of augmented reality in healthcare are where things get exciting. This isn’t science fiction; AR is an active tool being used right now to solve stubborn problems in surgery, medical training, and patient care.
Think of AR in surgery as a kind of high-tech GPS for the human body. By overlaying 3D anatomical models from a patient’s CT or MRI scans directly onto them, surgeons get a view that was previously unimaginable. This helps them guide their instruments with incredible precision during complex operations, reducing risk and improving outcomes.
Revolutionizing Surgical Precision and Planning
The operating room is where AR truly shines. In fact, surgical planning and guidance is the single biggest application in the AR healthcare market, making up a massive 42.45% of total revenue in 2024. It’s also growing at an impressive 29.01% each year, a number that tells you just how essential this technology is becoming in modern surgery.
With AR, surgeons can now:
- Visualize Hidden Structures: They can overlay 3D models of blood vessels, tumors, or organs right onto the patient. It’s like having X-ray vision, allowing them to navigate around critical structures with much greater confidence.
- Improve Accuracy: AR provides precise digital guides for incisions and placements. This is a game-changer in delicate fields like neurosurgery and orthopedics, where every millimeter counts.
- Collaborate Remotely: An expert surgeon from halfway across the world can see what the on-site surgeon sees and provide real-time guidance, drawing annotations directly into their field of view.
This depth of information is turning surgery into a far more data-driven practice, moving it away from guesswork and toward predictable, precise execution.
Transforming Medical Education and Training
AR is also completely changing how we train the next generation of doctors and nurses. Medical education has always depended on textbooks, diagrams, and cadavers, but AR offers a dynamic and interactive way to learn that just sticks better.
Instead of just reading about the heart, a student can now virtually hold it in their hands, peel back its layers, and watch it beat in real-time. This kind of immersive experience creates a much deeper, more intuitive understanding of how the body works.
This approach gives trainees a safe space to practice procedures over and over without any risk to a real person. This hands-on virtual learning helps them build skills and confidence long before they ever step into a live clinical setting. Our experience building an MDT planning app, for instance, shows how specialized software can foster this kind of collaborative, data-rich environment for clinical teams.
Enhancing Patient Care and Communication
The benefits of AR extend right to the patient’s bedside. For a common procedure like placing an IV, a nurse can use an AR device to see a patient’s veins clearly through their skin. This makes the process faster, more accurate, and a lot less painful, which is a huge win for both the patient and the staff.
AR is also helping to close the communication gap between doctors and patients. Instead of trying to explain a complex diagnosis with a confusing chart, a doctor can pull up a 3D model of the patient’s own organ. Seeing the problem firsthand helps patients grasp their condition and treatment plan, making them feel more empowered and involved in their own health journey. Ultimately, the best technology is the kind that improves human interaction, and AR is doing just that.
The Real-World Impact of AR in Healthcare
Bringing augmented reality into a clinical setting isn’t just about flashy new tech. It’s about getting real, measurable results that make a difference across the board—from better patient outcomes and faster medical training to smarter, more efficient hospital operations. When you look at the advantages, it becomes clear that AR is a serious investment in safety, education, and the financial health of an institution.
For patients, the changes are immediate and personal. AR-guided procedures mean fewer surgical errors and more precise diagnoses, which naturally lead to better treatment plans. It often allows for less invasive techniques, and that means one thing: getting back on your feet faster.
Raising the Bar for Patient Outcomes and Safety
If there’s one reason to get excited about augmented reality in health care, it’s the direct impact on patient well-being. By giving a surgeon real-time anatomical information overlaid directly onto their view of the patient, AR cuts down on the potential for human error in a huge way. We’re not talking about a small adjustment; this is a fundamental shift in surgical precision.
This level of enhanced visualization leads to some critical improvements:
- Fewer Complications: Surgeons can see exactly where delicate structures like nerves and blood vessels are, helping them navigate with confidence and avoid accidental damage.
- Faster Procedures: With a clear visual map, surgeries often move more quickly and smoothly. That means less time under anesthesia for the patient.
- More Accurate Diagnoses: AR can take a 3D model from a CT or MRI scan and project it right onto a patient’s body, giving clinicians a much clearer picture of the problem than flat, 2D images ever could.
This kind of accuracy is a game-changer in specialties like neurosurgery or oncology, where a single millimeter can be the difference between success and failure. The end result is simple: better health outcomes for patients.
Speeding Up Medical Training and Skill Development
Outside the operating room, AR is creating a powerful, risk-free training environment for the next wave of doctors and nurses. It turns dry textbook diagrams into interactive, hands-on learning, letting students and residents build real skills and confidence much faster than traditional methods allow.
AR creates a sandbox where trainees can run through complex scenarios over and over without ever putting a real patient at risk. They can perform virtual dissections, rehearse surgical steps, and learn to handle emergencies, all while building muscle memory and sharp clinical instincts.
This immersive practice helps close the gap between knowing the theory and actually being able to do the job. It ensures that when clinicians finally walk into a real procedure, they’re far more prepared. The market numbers tell the story: valued at just USD 610 million in 2018, the healthcare AR market is projected to shoot past USD 4.2 billion by 2026. This explosive growth is happening because the technology has proven its worth in both the classroom and the clinic. Discover more insights about AR/VR industry stats.
Creating Operational Efficiency and Cutting Costs
For hospitals and clinics, all these clinical improvements add up to smarter operations and very real cost savings. When you have smoother workflows, shorter procedure times, and fewer post-op complications, the financial benefits follow. Turning this new data into actionable insights with the right business intelligence services is how organizations can truly capitalize on using AI for your business.
The logic is straightforward. More efficient procedures mean an operating room can handle more cases, boosting throughput. More effective training gets new staff up to speed faster, which lowers onboarding costs. Most importantly, by preventing expensive complications and readmissions, AR reduces the overall financial strain on the healthcare system. As an experienced AI solutions partner, we’ve seen firsthand how smart tech integrations deliver a clear and compelling return on investment.
To put it all in perspective, here’s a quick summary of how AR benefits everyone involved.
AR Benefits Across Healthcare Domains
| Domain | Key Benefit | Practical Example |
|---|---|---|
| Patients | Enhanced Safety & Faster Recovery | A surgeon uses an AR overlay to see a 3D map of a tumor during removal, ensuring all of it is excised without damaging nearby healthy tissue. |
| Providers | Improved Precision & Decision-Making | A physician projects a patient’s CT scan onto their body to accurately locate a vein for an IV line on the first try, reducing patient discomfort. |
| Institutions | Reduced Costs & Better Training | A medical school uses AR simulations to train students on complex surgical procedures, cutting the need for expensive cadavers and physical models. |
Ultimately, AR creates a virtuous cycle where better care leads to better efficiency, benefiting the entire healthcare ecosystem.
Your Roadmap for Implementing AR Technology
Bringing augmented reality into a clinical setting isn’t something that happens overnight. It requires a thoughtful, strategic plan. Think of it less as flipping a switch and more as a journey—one that, when broken down into manageable stages, turns a daunting project into a series of achievable wins. This phased approach is key to demonstrating value early, managing risk, and building the momentum you need for wider adoption.
Here’s a practical, four-stage roadmap to guide you from initial idea to full-scale rollout.
Stage 1: Identify the Highest-Impact Use Case
Before you even think about headsets or software, you need to answer a fundamental question: What problem are we trying to solve? The biggest mistake is trying to boil the ocean by implementing AR everywhere at once. Don’t. Start small. As we explored in our AI adoption guide, selecting the right initial project is critical.
Pinpoint a specific department or clinical process where the return on investment is undeniable. Where is the need most acute? Good places to look often include neurosurgery, complex orthopedic procedures, or even medical training programs where hands-on experience is critical. By zeroing in on a single, high-impact area, you can build a rock-solid business case that gets key stakeholders excited and on board.
Stage 2: Select the Right Technology Partner
Once you have your target, it’s time to find the right partners. This is about so much more than just picking a cool piece of hardware. You need a technology team that genuinely understands the unique pressures and regulations of the medical world.
It’s absolutely critical to work with experts in healthcare software development. They need to live and breathe compliance issues like HIPAA and know how to make a new AR solution play nicely with your existing Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems. A great tool that doesn’t integrate is just a shiny paperweight. The goal is a solution that feels like a natural extension of a clinician’s workflow, not another hurdle. This often means building custom tools, so a deep understanding of mobile application development is invaluable for creating intuitive apps for tablets or smart glasses.
The right partnership can unlock some serious benefits across the entire organization.

As you can see, a well-planned AR strategy is a direct line to better patient outcomes, faster training, and smoother operations.
Stage 3: Launch a Pilot Program
With a clear use case and a solid partner, you’re ready to test the waters. A pilot program is your chance to see how the solution performs in a real clinical setting, not just a lab. This is where you’ll get invaluable feedback from your staff and uncover any challenges you couldn’t have possibly predicted.
Think of this stage as a learning lab, not a final exam. The goal isn’t a flawless rollout; it’s about refining workflows, tweaking the user interface based on what clinicians actually need, and proving the technology’s value on a small scale before you ask for a bigger budget.
Don’t skimp on training here. Your main objective is to make sure your clinical teams feel confident and supported. If they’re excited about the technology, you’re already halfway to success.
Stage 4: Measure Success and Plan for Scaling
Finally, you need to measure what matters. Define your key performance indicators (KPIs) from the very beginning. Are you tracking reductions in surgical time? Improvements in diagnostic accuracy? Higher proficiency scores for trainees? This hard data is what will ultimately prove the project’s ROI.
Once you have compelling results from your pilot, you can build a strategic plan to scale the technology to other departments. The best part? You can use all the lessons you learned from the pilot to make every future implementation faster, smoother, and even more effective.
Getting Past the Hurdles of AR Adoption
For all its promise, bringing augmented reality into a hospital or clinic isn’t as simple as flipping a switch. Like any major tech rollout, the path from a great idea to a daily clinical tool is filled with real-world obstacles. You have to think about the cost, the technical headaches, the security risks, and, most importantly, the people who will actually use it.
The first wall many organizations hit is the price tag. Let’s be honest—high-end AR headsets, sophisticated software, and the a team to get it all running isn’t cheap. Securing that kind of budget requires a rock-solid business case showing exactly how the investment will pay off in the long run.
Tackling the Technical and Security Maze
Beyond the initial sticker shock, the issue of data security is a deal-breaker. AR tools in a medical setting will inevitably handle Protected Health Information (PHI), and that brings a mountain of regulatory responsibility. Making sure the system is buttoned up and HIPAA compliant is non-negotiable. It means strong encryption and secure networks are table stakes to prevent a catastrophic data breach.
Then there’s the challenge of making the new tech play nice with the old. Hospitals are a complex web of existing IT systems, especially the all-important Electronic Health Records (EHRs). The new AR platform has to seamlessly plug into this ecosystem, not create another data silo.
This integration puzzle is often where specialized help comes in. Partnering with firms that live and breathe AI development services can be a smart move. They bring the expertise to ensure the AR solution fits neatly into existing workflows while meeting the incredibly strict security and interoperability demands of healthcare. The goal is to make life easier for clinicians, not give them another system to fight with.
Winning Over the People on the Front Lines
At the end of the day, even the most brilliant technology is useless if people won’t use it. You can’t just drop a new tool on a team of busy doctors and nurses and expect them to embrace it. Clinicians are creatures of habit for a reason—their workflows are tested and proven. If a new AR system feels clunky or slows them down, it will end up collecting dust.
So, how do you get everyone on board? It comes down to a smart, people-focused strategy:
- Start Small: Don’t try to boil the ocean. Kick things off with a pilot program in one specific department. This lets you prove the concept, iron out the wrinkles, and build a success story that gets others excited.
- Focus on User Experience (UX): The interface has to be dead simple. Work with designers who actually understand what a day in the life of a surgeon or a nurse looks like. The tool should feel like an extension of their skills, not a burden.
- Train, Train, and Train Again: Invest in proper, hands-on training. Give your staff the time and support they need to feel completely comfortable and confident with the new technology.
Facing these financial, technical, and human challenges head-on is what separates a successful AR implementation from a frustrating failure. We’ve learned from our own client cases that a thoughtful plan makes all the difference.
As incredible as today’s uses for augmented reality in healthcare are, we’re really just scratching the surface. What we’re seeing now is only the opening act. The real magic will happen as AR gets smarter and more deeply integrated into the day-to-day grind of clinical work.
We’re moving toward an era where AR and artificial intelligence work together. Imagine tools that can give a doctor diagnostic suggestions in real-time during an exam or highlight a subtle anomaly the human eye might have missed.

This fusion is setting the stage for truly personalized medicine. Picture this: a surgeon wears an AR headset that visualizes a patient’s unique genetic markers or even simulates how their body might respond to a particular drug on a cellular level. This isn’t science fiction. It’s the end of one-size-fits-all treatment and the beginning of care that’s fine-tuned for each individual person.
From Reactive to Predictive Care
The future of augmented reality in health care isn’t just about seeing the human body differently; it’s about seeing into the future. By combining AR with powerful analytics, a clinician could soon see predictive health models laid directly over a patient’s body.
Think about what that means. A doctor could spot potential disease progression or identify risk factors long before any symptoms show up. It’s a complete shift from reacting to illness to proactively keeping people healthy in the first place.
Of course, making this a reality demands a serious technological backbone. You need systems that can handle and display incredibly complex data in the blink of an eye. This is where expertise in building platforms with SaaS Consulting and reliable cloud services becomes absolutely critical.
The Rise of Telesurgery and Global Collaboration
AR is also on track to completely change what “remote care” means. It will soon be common for a top specialist in a major city to guide a local surgeon through a delicate operation from halfway across the world.
This is called telesurgery. The technology uses AR to project the expert’s hands and precise instructions right into the on-site surgeon’s view, creating a shared workspace that feels like they’re in the same room.
This approach breaks down geographical barriers. It’s a way to bring elite medical expertise to underserved communities and give everyone access to world-class care, no matter where they live.
The future we’re heading toward is one where healthcare is predictive, precise, and profoundly personal—with AR at its core. To stay ahead of the curve, healthcare providers need a partner who gets both the clinical challenges and the technical details. Finding the right AI solutions partner can help your organization not just keep up with these changes, but lead the way in turning these futuristic ideas into everyday, life-saving realities.
At Bridge Global, we build the sophisticated software that will power the future of healthcare. From compliant healthcare software development to advanced AI integration, we help you bring your vision to life. Explore our services and start building the future today.



