A Guide to Medical Imaging AI in Modern Healthcare
At its heart, medical imaging AI is about applying smart algorithms: specifically, a type of AI called deep learning, to interpret medical scans like X-rays, CTs, and MRIs. Think of it as a highly trained assistant for radiologists, one that helps them catch diseases earlier, sharpen their diagnostic accuracy, and simply manage the ever-growing mountain of scans.
Diagnostics Are Changing, and AI Is Leading the Way
Imagine a reality where patient diagnoses are not only faster and more accurate but also less of a strain on the clinicians making the calls. This isn't science fiction. It's what's happening right now with medical imaging AI, which has moved from a futuristic concept to a practical tool in today's diagnostic toolkit.
The sheer volume of medical imaging has skyrocketed, leaving radiologists buried under a workload that's frankly overwhelming. With this immense pressure comes a real risk of burnout and, worse, diagnostic errors. AI steps into this high-stakes environment not to replace anyone, but to act as a clinical co-pilot, augmenting the irreplaceable expertise of medical professionals.
A Partnership Between Human and Machine
The real magic of AI here is its ability to take on the repetitive, time-sucking tasks that are tough for the human eye to sustain. It can tirelessly sift through thousands of images to flag tiny anomalies, measure changes in tumor size with a precision that’s beyond human capability, and triage the most urgent cases so they get seen first.
This frees up radiologists to concentrate their skills on the truly complex cases that demand deep clinical judgment. As a leading AI solutions partner, we see this human-machine collaboration as the clearest path to better patient outcomes.
By automating routine analysis and highlighting areas of concern, AI empowers clinicians to work more efficiently and confidently, ultimately improving the quality and speed of care.
The market is betting big on this potential. The AI in the medical imaging space is expected to jump from USD 2.43 billion in 2026 to an incredible USD 29.95 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 36.91%. You can dig into more of this data over at Fortune Business Insights.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from the core mechanics to real-world implementation strategies. As we’ve covered in our look at AI trends shaping the healthcare industry, adopting these tools is quickly becoming a strategic must-have. We'll break down the technologies, applications, and frameworks that can help your organization succeed in this new diagnostic landscape.
How Does Medical Imaging AI Actually Work?
So, how does an AI go from a raw pixelated image to a life-saving insight? It's not magic, but a methodical process where algorithms are trained to see and interpret medical scans. Think of it like a radiologist in training, but one that can review millions of cases at a speed no human could ever match. The entire process starts with the images themselves.
Every type of scan: an X-ray, CT, or MRI, tells a different story. X-rays are great for dense structures like bone, while an MRI gives us an incredibly detailed look at soft tissues. For an AI to make sense of any of this, it needs to learn from a massive, high-quality library of images that have been painstakingly annotated by medical experts. This is how the algorithm learns the difference between a healthy lung and one with a suspicious nodule.
The Three Core Jobs of a Medical AI
Once the AI is trained, it generally focuses on three primary tasks. Each one is a bit more complex than the last, but together they form the foundation for almost every application in the field.
To make these concepts clearer, let's break down what the AI is actually doing with the images. The table below uses some simple analogies to explain these core functions.
Core AI Tasks in Medical Imaging Explained
| AI Task | What It Does | Simple Analogy | Clinical Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Detection | Points out potential areas of interest or anomalies in an image. | A security guard spotting something unusual on a camera feed. | Flagging a tiny, suspicious spot on a mammogram that needs a closer look. |
| Segmentation | Precisely outlines the exact boundaries of a specific object or region. | Tracing the exact shape of a lake on a satellite map. | Drawing a precise border around a brain tumor to plan for surgery or radiation. |
| Classification | Categorizes a detected anomaly based on its characteristics. | A quality inspector sorting apples into “good,” “bruised,” or “rotten” bins. | Determining if a detected skin lesion is benign, pre-cancerous, or malignant. |
These foundational skills are the building blocks that empower the sophisticated diagnostic tools we see today. If you want to dive deeper into the technical side, this guide on AI image analysis offers a great look at how these systems process visual data.
The Technology Behind the ‘Eyes’ of AI
The workhorse behind these abilities is a special type of artificial intelligence called a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). These networks are actually inspired by how the human brain’s visual cortex works, making them exceptionally good at finding patterns in images.
A CNN doesn’t see a whole image at once. Instead, it breaks it down into tiny pieces, analyzing pixels to identify simple things like lines, edges, and textures. Then, it combines these simple features to recognize more complex shapes, like the specific outline of an organ or the unique texture of a tumor. It’s the same way we learn to recognize a face: we see eyes, a nose, a mouth, and our brain puts them together. The CNN does this for medical anomalies.
What makes CNNs so powerful in medicine is their knack for spotting incredibly subtle patterns in the data, patterns that might be completely invisible to the human eye. This could be the key to catching diseases earlier than ever before.
Building and fine-tuning these complex networks takes serious computational power and deep expertise. It’s the kind of specialized work we’ve explored in our broader guide on how machine learning can be a game-changer for businesses. At the end of the day, the goal is always the same: to build a reliable tool that fits right into a doctor’s workflow, providing clear, actionable information that helps them make better, faster decisions.
Building and Validating a Medical AI Model
You don’t just “build” a medical AI model. It’s more like cultivating a highly specialized expert, and that process is painstaking, cyclical, and demands a real marriage of clinical and technical skills. It all starts with the right foundation: data. We’re talking about massive, high-quality, and ethically sourced collections of medical images.
This dataset can’t be one-dimensional. It needs to reflect the real world, which means including a wide mix of patient demographics, different types of imaging equipment, and a whole spectrum of clinical scenarios. If you don’t get this part right, you risk building an algorithm that’s biased and completely unreliable in a real clinical setting.
Once you have the data, the real “teaching” begins with annotation. This is where radiologists and other clinical specialists manually label the images, meticulously outlining tumors or flagging tiny fractures. They are, in essence, transferring decades of diagnostic experience into a format the algorithm can understand. The old saying “garbage in, garbage out” has never been truer; the quality of this human-led annotation directly dictates how good the model can ever be.
From Training to Trustworthiness
With a carefully annotated dataset in hand, the model is ready for training. It’s an iterative process where the algorithm chews through the labeled images again and again, learning to spot the subtle patterns that signal a specific condition. We constantly tweak and refine its parameters, pushing it to become more and more accurate.
But a trained model is just a starting point. The most critical phase is validation; proving that this tool is not just clever, but also safe and dependable enough for patient care. It’s a journey from potential to proven performance. As we explored in our guide, a huge piece of this is baking in ethical principles from the very beginning, which is central to responsible AI development.
The workflow for building and validating a medical imaging AI typically moves from identifying an issue to classifying it, helping a clinician make a final call.
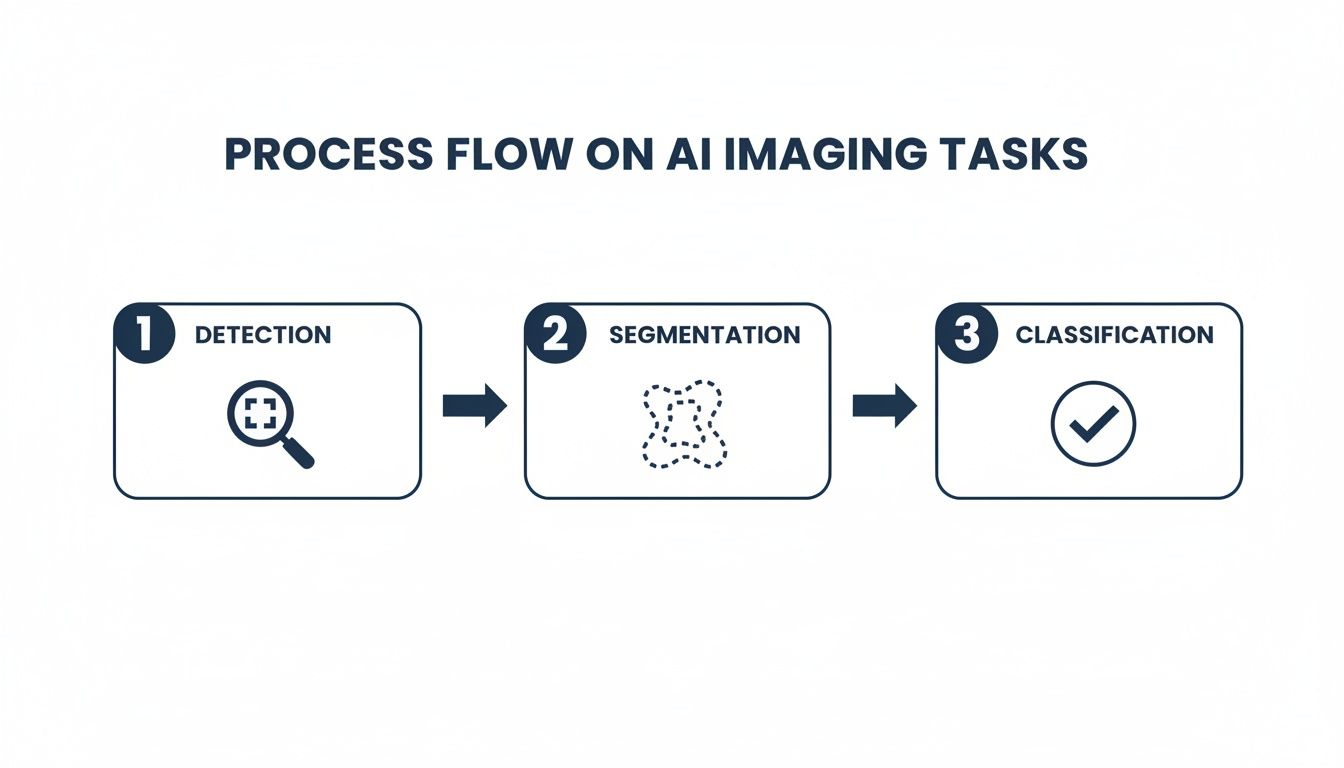
This flow shows how each task builds on the last, turning raw pixels into actionable clinical insights.
Measuring What Matters in a Clinical Context
When we validate a medical AI, we look at performance metrics that go much deeper than simple accuracy. In a hospital, the kind of mistake a model makes has serious consequences.
-
Sensitivity (True Positive Rate): How good is the model at catching the disease when it’s actually there? For a screening tool, you need incredibly high sensitivity. You’d much rather have a false alarm than miss a real case (a false negative).
-
Specificity (True Negative Rate): How good is the model at correctly identifying healthy patients? High specificity is key to preventing unnecessary stress, costly follow-up tests, and patient anxiety caused by false alarms (false positives).
Finding the right trade-off between sensitivity and specificity isn’t a technical problem; it’s a clinical one. It requires weighing the clinical risk of a missed diagnosis against the burden of a false alarm for that specific disease.
Navigating the Regulatory Gauntlet
Finally, no medical AI tool sees the light of day without getting through a maze of regulations. In the United States, these tools are considered Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) and are governed by the FDA. Earning FDA clearance is a monumental task that requires exhaustive documentation and clinical evidence to prove the model is both safe and effective for what it claims to do.
On top of that, any system handling patient data must be completely compliant with privacy laws like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This is non-negotiable. Protecting sensitive patient information is paramount at every single step. Successfully navigating this complex landscape is one of the most challenging parts of the process, and it’s a core focus of our work with clients.
Integrating AI into Your Clinical Workflow
A brilliant medical imaging AI model is only valuable if it actually gets used. It has to fit seamlessly into a clinician’s daily routine. Let’s be honest; the most powerful algorithm on the planet is useless if it creates friction, adds extra clicks, or disrupts well-established processes. Success isn’t just about accuracy; it’s about thoughtful integration that makes the technology feel like a natural extension of the existing clinical environment.
This means bridging the gap between the AI platform and the core systems that run a modern hospital. The two most important are the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS), which is the digital hub for all medical images, and the Electronic Health Record (EHR), the comprehensive patient chart. When done right, AI-generated insights appear directly within these systems, right where clinicians are already looking.

Choosing Your Deployment Strategy
When you decide to bring AI into your infrastructure, you’ll face a fundamental choice: deploy it on your own servers or use a cloud-based solution. Each path has distinct trade-offs related to security, cost, and scalability. The right answer really depends on your organization’s specific needs and resources.
-
On-Premise Deployment: This is the traditional route, where you host the AI software and process data on your own local servers. The big win here is maximum control over data security, and it can be faster for processing massive image files locally. However, it requires a significant upfront investment in hardware and a dedicated IT team to handle maintenance and updates.
-
Cloud-Based Deployment: Using cloud services from providers like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure offers incredible flexibility. You pay for what you use, which sidesteps huge initial hardware costs. While updates are simplified, this approach demands a rock-solid network and meticulous management of data privacy in a third-party environment.
This decision is especially relevant in a market like North America, which is setting the pace for global AI adoption. The region’s advanced infrastructure and strong cloud partnerships are key reasons for its leadership. According to one report, it captured 37.9% of the market’s revenue share in 2024, with the U.S. alone projected to hit around USD 0.90 billion in 2026. You can find more details on this trend from Fortune Business Insights.
Designing for Humans, Not Just Machines
Beyond the technical plumbing, the best integrations put the user first. The interface has to be intuitive, presenting AI findings in a way that is clear, actionable, and trustworthy. If a tool frustrates a clinician or slows them down, it will be abandoned, no matter how accurate its model is.
The goal is to design a workflow where the AI operates quietly in the background, surfacing critical information at precisely the right moment without adding cognitive load to the user. This human-centered approach is the difference between a tool that is merely adopted and one that is truly embraced.
This kind of deep integration, which blends powerful technology with practical usability, is a core principle of effective healthcare software development. It’s about building tools that truly empower medical professionals, making their work easier and more effective. By focusing on how the AI fits into the human side of medicine, we ensure it actually delivers on its promise to improve patient care.
Measuring the True Impact and ROI of AI
Justifying a major investment in medical imaging AI means you have to look well beyond the initial price tag. To build a compelling business case, you need a full picture of the Return on Investment (ROI) – one that captures both the hard numbers and the invaluable, less-tangible benefits that ripple across the entire organization.
Success here isn’t just about saving money. It’s about building a smarter, more effective, and more sustainable clinical workflow. The real value emerges when AI empowers your clinicians, directly improves patient care, and strengthens the operational backbone of your imaging department. This complete view is what gets stakeholders to see the real potential of AI for your business.
Quantifying the Tangible Gains
The clearest way to measure ROI is through metrics you can count. These are the operational wins that show up directly on balance sheets and performance dashboards, providing the hard data needed to prove the technology’s financial and logistical worth.
Key tangible metrics to track include:
-
Faster Report Turnaround Time (TAT): AI is brilliant at triaging urgent cases and automating routine measurements. This can slash the time from scan to report, often turning hours into minutes and directly speeding up patient treatment decisions.
-
Increased Radiologist Throughput: By offloading tedious tasks, AI lets radiologists focus on interpreting more studies each day without compromising quality. A bump of even 10-15% in throughput can make a huge difference in clearing backlogs.
-
Improved Resource Utilization: AI-driven insights can help optimize scanner schedules and patient flow, making sure your expensive imaging equipment is running at full tilt and maximizing the return on those big capital investments.
Looking Beyond the Bottom Line at Qualitative Value
While the financial metrics are critical, it’s often the qualitative benefits of AI that leave the most lasting mark on a healthcare organization. These gains are about improving the human side of medicine: boosting morale, sharpening clinical confidence, and raising the bar for patient care.
These less-tangible benefits include:
-
Reduced Radiologist Burnout: Automating the monotonous, repetitive parts of the job significantly lightens the cognitive load on radiologists. This is a direct strategy for fighting burnout and improving long-term job satisfaction.
-
Enhanced Diagnostic Confidence: Think of AI as a second set of eyes, flagging subtle findings a person might overlook. This safety net gives clinicians greater confidence in their final diagnoses.
-
Better Patient Outcomes: This is the ultimate goal. Earlier, more accurate diagnoses led directly to better treatment results. It’s the most important outcome, even if it’s the hardest to assign a specific dollar value to.
The true ROI of medical imaging AI is a blend of operational efficiency and clinical excellence. It’s about creating a system where technology supports clinicians, leading to faster, more accurate diagnoses and ultimately, a higher standard of care for every patient.
Building a Strong Business Case with Real-World Examples
To make the ROI feel real, it helps to connect it to specific clinical scenarios where AI is already delivering undeniable value.
Take oncology, for example. AI-powered tools can segment and measure tumor volume with a speed and precision that’s simply not possible by hand. This gives oncologists a much clearer picture of how a treatment is working, allowing them to adjust care plans much faster.
Or look at cardiology, where AI can automate the calculation of key metrics like ejection fraction from echocardiograms. This frees up precious time for cardiologists and sonographers, letting them see more patients and cut down wait times for critical cardiac assessments.
Understanding how to effectively measure and demonstrate the ROI of AI integration is crucial for getting buy-in. Working with a partner skilled in AI development services can help you frame this value proposition in a way that resonates with every stakeholder.
Your Roadmap for AI Implementation
Bringing an AI initiative for medical imaging to life can feel like a huge undertaking. The key is breaking it down into a structured, phased approach. Think of it less as a giant leap and more as a manageable journey, with a clear roadmap to make sure your investment hits the mark, delivers real value, and gets adopted by your clinical teams. This method takes the risk out of the project, letting you prove the concept at each stage before going all-in.
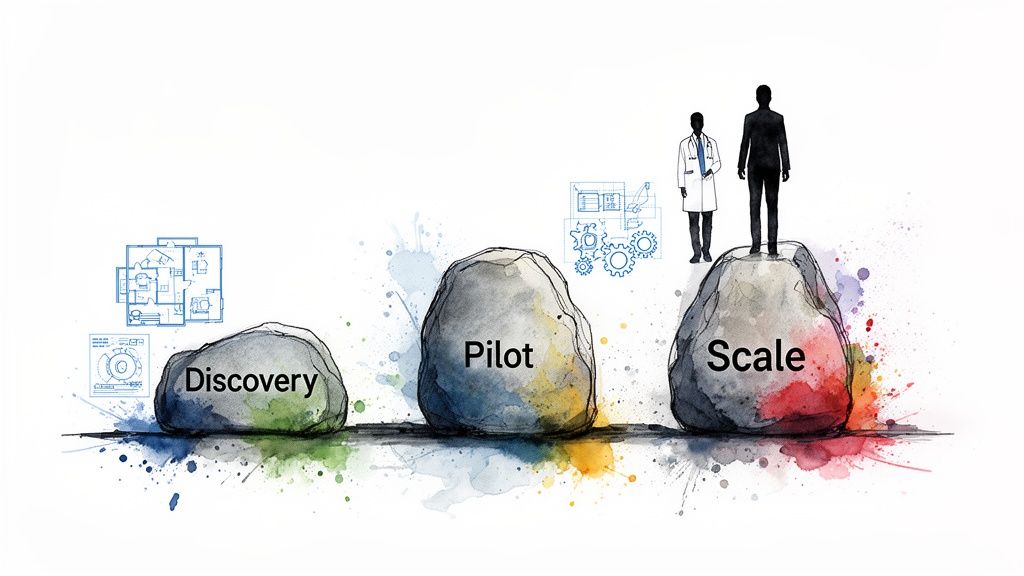

This journey doesn’t start with lines of code; it starts with a conversation. A successful project begins by zeroing in on a specific, high-impact clinical problem that AI is genuinely suited to solve. Having the right partner here is critical – someone to help you see the possibilities and map out a clear path forward.
Phase 1: The AI Discovery Workshop
The first, foundational step is a collaborative AI discovery workshop. This is where we get everyone in the same room: clinical stakeholders, your IT team, and our AI experts. The goal is to get past vague ideas and pinpoint a concrete problem where AI can make a measurable difference, whether that’s slashing diagnostic turnaround times or automating monotonous but critical measurements.
During this phase, we help you get answers to the big questions:
-
Where are the most significant bottlenecks in our clinical workflow?
-
What kind of data do we have available to train and validate a model?
-
What does a “win” actually look like, and how will we measure it?
This initial deep dive is all about setting a solid direction and making sure the entire project is anchored in real-world clinical needs from day one. It’s the strategic blueprint for everything that follows.
Phase 2: The Pilot Project
Once you’ve identified a high-value use case, it’s time to build a pilot project, often called a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). This is a focused, smaller-scale version of the final solution, built specifically to prove the concept in a controlled setting. A pilot lets you test the AI model’s real-world performance, get crucial feedback from clinicians, and smooth out any integration wrinkles without disrupting the entire department.
A successful pilot gives you something tangible to show for your efforts. It provides hard evidence of the AI’s value, which creates a powerful business case for more investment and builds momentum with stakeholders across the organization.
Phase 3: Scaling Across the Enterprise
With a successful pilot under your belt, you’re ready to scale. This is the phase where you expand the AI solution for wider use, which demands robust engineering and a solid grasp of enterprise-level IT. This is where expertise in custom software development and specialized healthcare software development becomes a massive advantage.
Working with an experienced AI solutions partner ensures your final tool isn’t just clinically effective but also secure, scalable, and smoothly integrated into the workflows your team already uses. By taking a collaborative approach, informed by practical examples from our client cases, we can help ensure your medical imaging AI project achieves lasting success.
Frequently Asked Questions About Medical Imaging AI
What are the main applications of AI in medical imaging?
AI in medical imaging primarily focuses on three core tasks: Detection, where it identifies potential anomalies like nodules or fractures; Segmentation, where it precisely outlines organs or tumors for treatment planning; and Classification, where it categorizes findings, such as distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions. Together, these tasks help automate analysis and support clinical decisions.
Is AI intended to replace radiologists?
No, the consensus is that AI will augment, not replace, radiologists. AI excels at handling high-volume, repetitive tasks, which helps reduce workload and burnout. This frees up radiologists to focus on complex case interpretation, interdisciplinary collaboration, and patient consultation, ultimately enhancing their diagnostic capabilities and efficiency.
How is medical imaging AI regulated for patient safety?
Medical imaging AI tools are typically classified as Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) and are rigorously regulated by bodies like the FDA in the United States. Manufacturers must provide extensive clinical evidence to prove their algorithms are safe and effective before they can be approved for clinical use. Additionally, all solutions must comply with strict data privacy laws like HIPAA to protect patient information.
What are the first steps to implementing AI in a clinical setting?
The best approach is to start small with a well-defined problem. Identify a specific, high-impact clinical bottleneck or a repetitive, time-consuming task that AI could automate. A great first step is an AI Discovery Workshop with a technology partner to identify the best use case. From there, you can launch a pilot project to test the solution in a controlled environment, prove its value, and build a strong business case for a full-scale rollout.
Ready to see what medical imaging AI can do for your organization? At Bridge Global, we help turn these complex ideas into practical, compliant, and genuinely useful healthcare solutions. Let’s discuss your vision today.