Hospital System Integration Services for Modern Healthcare
Hospital system integration services are the glue that holds a modern hospital’s technology together. At its core, this service connects all the separate software systems, from admissions and labs to the pharmacy and billing, so they can talk to each other and share data automatically. This creates a single, unified digital backbone for the entire facility, which is absolutely critical for preventing medical errors and boosting efficiency. It’s the first real step toward providing the kind of data-driven care patients expect today.
Why Disconnected Hospital Systems Create Chaos
Picture this: an ER doctor can’t access a new patient’s primary care records. The lab system can’t send results directly to the pharmacy. Billing must manually chase down information from three different departments. This isn’t just a worst-case scenario; it’s the frustrating reality for many hospitals struggling with siloed data. This kind of digital fragmentation leads to chaos, and the consequences can be severe.
Think of a hospital’s technology ecosystem like an orchestra. When each system, the Electronic Health Records (EHRs), imaging archives, and billing platforms, plays its own tune, you don’t get music. You get noise. This cacophony causes critical breakdowns in both patient care and daily operations.
The Real-World Consequences of Data Silos
This lack of coordination hits where it hurts most: patient safety and hospital performance. When a physician is forced to work with an incomplete patient history, the risk of prescribing the wrong medication or missing a key diagnostic clue goes way up.
Operationally, these disconnects create massive bottlenecks. We’re talking about longer wait times for patients, delays in getting critical lab results, and administrative headaches that burn out staff. These aren’t just minor inconveniences; they slowly chip away at patient trust and staff morale.
That’s why so many organizations are focused on modernising and future-proofing NHS facilities and similar initiatives worldwide. It’s about building a more resilient, connected healthcare infrastructure from the ground up.
The core problem is that disconnected systems force healthcare professionals to make critical decisions with incomplete information. This introduces unnecessary risk into nearly every patient interaction, from diagnosis to discharge.
The global healthcare community is moving fast to fix this. The Healthcare IT Integration Market shot up from USD 4.43 billion in 2023 and is on track to hit USD 12.97 billion by 2032. That’s a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.69%, signaling a massive industry-wide push to connect these fragmented systems.
System integration acts as the orchestra’s conductor, bringing all the different instruments together to create a single, reliable source of truth. As we explored in our guide on healthcare software modernization, this journey often starts with a smart strategy. By linking every digital touchpoint, hospitals finally get that seamless flow of information that helps clinicians do their best work, makes workflows smoother, and ultimately, saves lives.
The Blueprint For Connecting Healthcare Data
For different medical systems to actually talk to each other, they need a shared language. This technical foundation is the very backbone of hospital system integration, turning a jumble of separate applications into a single, cohesive network that shares data effortlessly. Without it, the data from an MRI machine would be complete gibberish to a patient’s electronic health record (EHR).
Think of it like international travel. You can’t just plug your hairdryer into a wall socket in another country; you need an adapter. In healthcare, data standards are those adapters. They translate information into a universal format that every connected system can understand, no matter who built it or what it does.
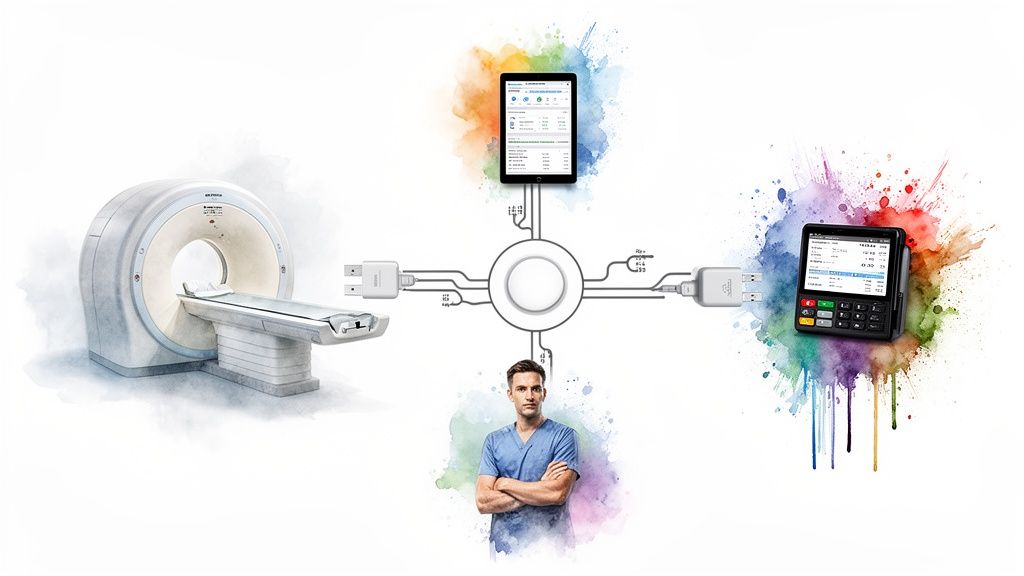
Core Communication Standards
Two main “languages” really run the show, governing the flow of nearly all clinical and administrative data today. Getting a handle on them is crucial for any hospital leader looking to build a smart integration strategy. These aren’t just technical terms; they’re the rules of the road that make sure a patient admission is recorded the same way in the billing system as it is on a doctor’s dashboard.
- HL7 (Health Level Seven): This is the old, reliable dialect of healthcare data. For decades, HL7 has been the workhorse for moving information like patient demographics, lab orders, and test results between different systems inside a hospital’s walls. It’s proven, dependable, and baked into most legacy systems.
- FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources): Think of FHIR as the modern, web-savvy language built for today’s connected world. It uses the same kind of technology (APIs) that power your favorite mobile apps, making it far easier for patient portals, smartphone apps, and cloud tools to securely grab and share data in real-time.
Our deep experience in healthcare software development means any solution we build is fluent in both of these critical standards. This ensures that brand-new tech can communicate flawlessly with the trusted systems you already have in place.
Common Integration Patterns
Beyond the language, the way you wire everything together matters. There are really two main ways to connect hospital systems, and each comes with its own set of pros and cons.
The first is the point-to-point model. Picture this: you run a separate, dedicated wire from your TV to your speaker, another from your game console to the TV, and so on. This approach creates a direct link between two systems, like your lab information system and the EHR. It’s simple for just one connection, but it quickly devolves into a chaotic mess as you add more and more systems.
A point-to-point architecture inevitably creates what IT pros call ‘spaghetti integration.’ For every new application you add, you have to build custom connections to all the other systems it needs to talk to. This gets expensive and incredibly fragile to maintain.
A much smarter, more scalable approach is the hub-and-spoke model. Here, a central integration engine acts as the main traffic controller, or the “hub.” Instead of connecting directly to one another, all your systems (the “spokes”) plug into this one central engine.
The Power of a Central Hub
The hub-and-spoke model changes the game. That central integration engine handles all the heavy lifting, translating data formats and routing messages to the right place. So, when your hospital wants to bring in a new pharmacy system, you only have to connect it once, to the hub, not to every other individual application.
This method delivers some serious advantages:
- Scalability: Adding new tools is straightforward and doesn’t break your existing connections.
- Maintenance: When something goes wrong, you have one central place to look, making troubleshooting much faster.
- Consistency: The hub acts as a gatekeeper, enforcing data standards and ensuring all information is formatted correctly before it’s passed along.
This is the blueprint for a truly connected hospital: universal standards like HL7 and FHIR providing the language, and a strategic hub-and-spoke architecture providing the framework. It’s how you transform isolated data points into a powerful, flowing stream of information that directly improves patient care and operational efficiency.
Choosing Your Integration Architecture
Building a truly connected hospital isn’t just about picking the right software; it’s about laying a solid architectural foundation. This choice is a big one, as it dictates how your data is stored, managed, and ultimately, protected. For hospital leaders, this decision usually boils down to three main paths: on-premise, cloud, or a hybrid model, each with its own trade-offs in security, scalability, and cost.
On-Premise, Cloud, or Hybrid?
Think of an on-premise architecture like owning your own private power plant. You have total control over every single wire and generator. That’s a huge plus. The downside? You’re also on the hook for all the maintenance, security, and upgrades. This model keeps all your sensitive data inside your own physical servers, which offers a high degree of control but requires a hefty upfront investment and a dedicated IT team to keep the lights on.
A cloud architecture, on the other hand, is like plugging into the public power grid. You get immediate, flexible access to massive resources without having to build a thing. It offers incredible scalability; you can easily ramp up computing power for a big analytics project and then scale back down. This model turns a large capital expense into a more predictable operating expense, which is often a big win for budgeting.
For many healthcare organizations, the smartest solution is found somewhere in the middle. A hybrid model gives you the best of both worlds. You can keep highly sensitive data, like patient records, on secure on-premise servers while using the cloud’s flexibility for other applications like patient portals or data analytics. It’s a balanced approach that doesn’t force an all-or-nothing decision.
This is where an Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) becomes a game-changer. An iPaaS acts as the central nervous system for your hospital, a cloud-based hub that directs the flow of data between all your different systems – whether they’re on-site or in the cloud. It handles the complex translations, routing, and security protocols, making everything work together as a single, cohesive unit. As we explored in our guide, a well-engineered core is fundamental to any modern digital health platform engineering strategy.
Comparing Integration Architecture Models
Choosing between these models involves weighing several critical factors. The right choice depends entirely on your organization’s specific needs, resources, and long-term goals. This table breaks down the key differences to help guide your decision.
| Factor | On-Premise | Cloud | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | High capital expenditure (CAPEX) for hardware and infrastructure. | Low to no upfront cost; based on a subscription model (OPEX). | Moderate; balances initial CAPEX with ongoing OPEX. |
| Control & Security | Maximum control over data, hardware, and security protocols. | Security is a shared responsibility with the cloud provider; less direct control. | High control over sensitive on-premise data, with cloud flexibility for other assets. |
| Scalability | Limited; requires purchasing and installing new hardware to scale. | High; resources can be scaled up or down on demand almost instantly. | Flexible; allows scaling of cloud components while maintaining core on-premise systems. |
| Maintenance | Full responsibility of the internal IT team for all updates and maintenance. | Managed by the cloud provider, reducing the burden on internal teams. | Shared responsibility; IT team manages on-premise, provider manages cloud. |
| Compliance | Full control and responsibility for meeting compliance standards like HIPAA. | Relies on provider’s compliance certifications (e.g., HIPAA BAA). | Complex; requires ensuring compliance across both environments. |
Ultimately, a hybrid approach often provides the most strategic advantage, offering a practical path to modernization without compromising the security of core patient data.
Why Getting This Right Is So Critical
The stakes are incredibly high. Hospitals represent a massive 64.32% share of the Healthcare IT Integration Market, and they’re the ones driving the need for these sophisticated solutions. A typical tertiary care center might be juggling hundreds of separate applications. Without a powerful integration engine, you get chaos.
This chaos has real-world consequences, like duplicate patient records, which cost U.S. hospitals a staggering $8.6 billion every year in wasted time and resources.
Compliance Must Be the Bedrock
No matter which architecture you choose, one thing is absolutely non-negotiable: compliance. Regulations like HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe aren’t just features you can bolt on later. They have to be the bedrock of your entire system.
Security and compliance must be designed into the system from day one. Retrofitting these critical protections after the fact is not only more expensive but also significantly less effective, leaving patient data vulnerable.
This means every single component, from the servers and databases to the APIs and data transmission protocols, must be built to meet or exceed these strict standards. This includes essentials like:
- End-to-end encryption to protect data both when it’s stored and when it’s moving.
- Robust access controls to make sure only authorized people can see sensitive information.
- Comprehensive audit trails that log every single interaction with patient data, creating a clear record of who did what, and when.
Your Step-By-Step Implementation Roadmap
Moving from high-level strategy to a live, functioning system requires a clear, practical plan. Integrating hospital systems isn’t a one-and-done event; it’s a carefully managed journey. I’ve broken down the process into four distinct stages to help you navigate this essential transformation without getting overwhelmed.
This phased approach turns a massive project into a series of manageable steps. Each one builds on the last, creating a connected, powerful, and secure digital environment for your hospital.
Stage 1: Discovery and Auditing
First things first: you need a detailed map of your current technology. Before you can build anything new, you have to understand what you’re working with. This means a full audit of every system you have, from your core EHR to the specialized software in your lab, radiology, and pharmacy departments.
During this discovery phase, your team needs to identify every single application, database, and data source. The goal is to see how information flows or, more often, doesn’t flow between these separate silos. You’ll need to answer a few key questions:
- Which systems hold the most critical patient or operational data?
- What data formats and standards (like HL7v2, CDA, etc.) are being used right now?
- Where are the biggest communication gaps and time-consuming manual workarounds?
This deep dive uncovers the real-world pain points and specific integration opportunities that will shape the entire project. It’s the foundation for designing a solution that actually solves problems for your staff and patients.
Stage 2: Strategy and Partner Selection
With a clear picture of your current state, you can start designing the future. This stage is all about defining the project’s scope, choosing the right architecture (on-premise, cloud, or a hybrid model), and most importantly, picking the right technology partner.
This is a decision you can’t afford to get wrong. Your partner needs more than just technical chops; they need a proven track record in healthcare. They must understand the nuances of standards like HL7 and FHIR and treat HIPAA compliance as non-negotiable.
A great integration partner is more than a vendor; they’re a strategic guide. They don’t just connect the pipes; they bring the industry insight to make sure the solution leads to real clinical and operational improvements.
Finding that right-fit partner is absolutely crucial for long-term success, a journey we’ve proudly navigated with many organizations, as you can see in our client cases.
Stage 3: Phased Rollout and Implementation
Trying to integrate everything at once is a recipe for chaos. A phased rollout is a much smarter strategy. It lets your organization score some quick wins and build momentum. Start with a workflow that’s high-impact but relatively low-complexity, like connecting your patient registration system directly to the EHR to speed up admissions.
Once that first piece is stable and working well, you can expand to other critical areas. This step-by-step approach minimizes risk, gives you room to learn and adjust, and shows tangible value to stakeholders right away. Each successful phase builds the confidence you need for the next one.
This flowchart shows the typical paths organizations take, often starting with on-premise systems and evolving toward more flexible cloud and hybrid models.
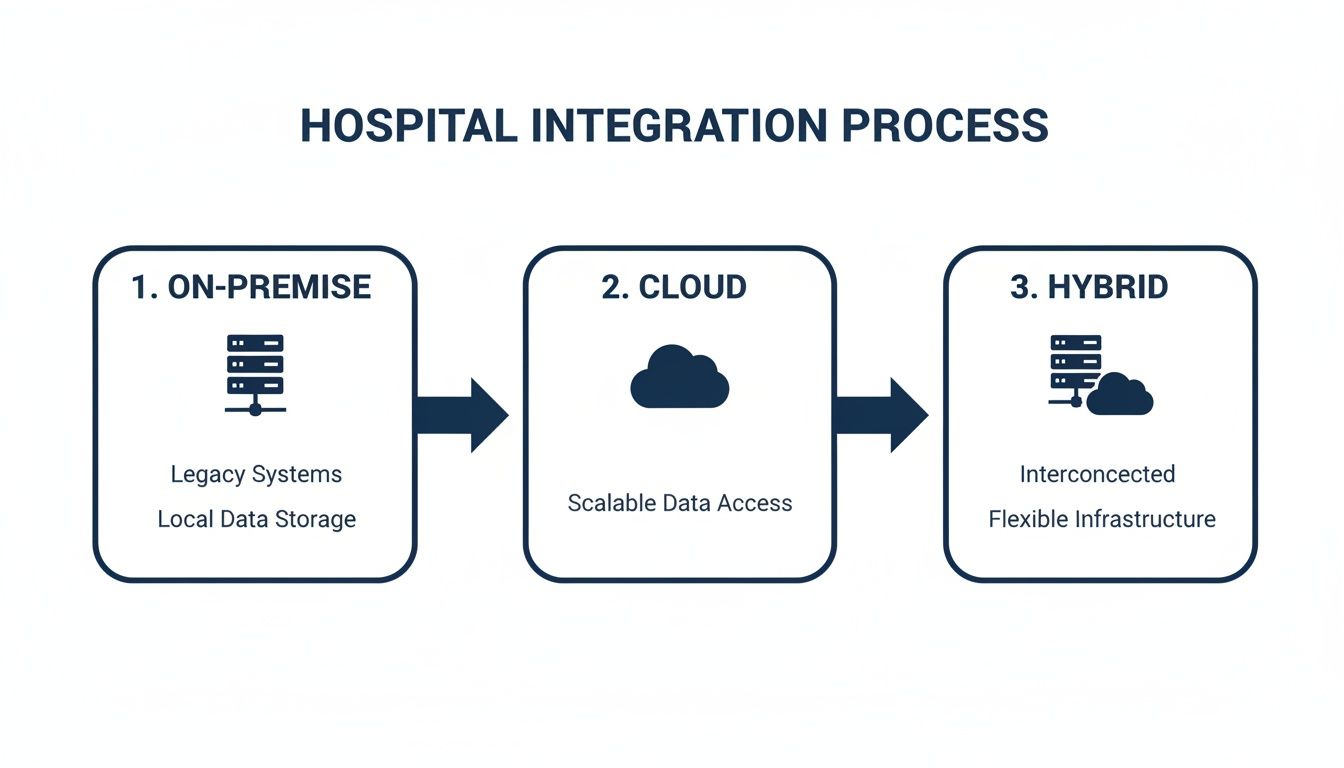
The takeaway here is that becoming a connected hospital is an evolution. It’s about blending the infrastructure you already have with the scalability and power of modern cloud services.
Stage 4: Ongoing Optimization and Monitoring
Integration isn’t a “set it and forget it” project. The real work begins after go-live. This final stage is all about continuous monitoring and optimization. You need to be tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the actual impact on things like patient wait times, billing accuracy, or administrative overhead.
Keep a close eye on data flow, system performance, and user feedback to spot areas for improvement. Your hospital’s needs will change, and new technologies will emerge. Your integration architecture has to be able to adapt. This final, ongoing stage is what ensures your investment keeps paying off for years to come, giving you a resilient digital foundation built for the future.
How AI Puts Your Integrated Healthcare Data to Work
Getting your hospital systems talking to each other is a huge win, but it’s not the final goal. True integration is about what you do with that newly connected data. It’s the foundation for Artificial Intelligence (AI) that can sift through oceans of information and pull out life-saving insights. Once data from your EHR, lab systems, and imaging archives can flow together, AI models can analyze it at a scale and speed that is simply beyond human capability.
This is where all the hard work of building an integrated system really starts to deliver. You move beyond just having connected “plumbing” and start getting into the realm of prediction. It’s a fundamental shift from reacting to health crises to proactively managing patient wellness before problems arise. This leap from connected data to actionable intelligence is what modern healthcare infrastructure is all about.

Unlocking Predictive Analytics
One of the first and most powerful applications for AI is its ability to spot trouble on the horizon. By crunching thousands of data points from a patient’s entire record: labs, vitals, medications, and even unstructured clinical notes, AI models can detect subtle patterns that point to a high risk of a specific event.
A classic example is predicting 30-day hospital readmissions. An AI can flag patients who are most likely to end up back in the hospital shortly after discharge. This gives your care teams a heads-up to intervene with targeted follow-up calls, home health visits, or medication checks, ultimately improving outcomes and avoiding costly penalties. These aren’t just theoretical benefits; the ROI is clear and measurable.
Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy
In specialties like radiology and pathology, AI is quickly becoming a trusted co-pilot for clinicians. A truly integrated system feeds the AI algorithm a patient’s complete imaging history alongside the full clinical context from the EHR. This rich, comprehensive dataset is what fuels its analytical power.
Think about an AI tool scanning thousands of X-rays or MRIs. It can flag tiny anomalies that a radiologist might miss, especially at the end of a long shift. The point isn’t to replace the expert; it’s to give them a powerful assistant that helps them spot disease earlier and with greater confidence.
By processing enormous datasets in seconds, AI essentially acts as a second set of eyes, helping clinicians confirm their findings and focus on the most complex cases. This blend of human expertise and machine precision is where diagnostic medicine is heading.
Automating Administrative and Operational Workflows
The power of AI isn’t just for the clinical side. All that integrated data can also be used to streamline the back-office tasks that drain time and resources, freeing up your staff to focus on patients.
- Intelligent Scheduling: AI can look at physician schedules, OR availability, and historical patient flow to build optimized appointment calendars that slash wait times and make the most of your resources.
- Automated Coding and Billing: Natural Language Processing (NLP) models can “read” a clinician’s notes and suggest the right medical codes for billing. This cuts down on human error and gets claims paid faster.
- Supply Chain Management: AI can predict the need for specific medical supplies by analyzing past usage and upcoming surgical schedules, helping to prevent a critical item from being out of stock when you need it most.
These applications tackle the operational bottlenecks that cost hospitals dearly. By turning raw data into intelligent automation, AI helps build a more efficient and responsive organization, as we detail in our guide to AI solutions for healthcare.
Measuring the Real-World Impact of Integration
An integration project is a serious investment. So, how do you prove it’s actually paying off? The value of hospital system integration services isn’t just a concept on a whiteboard; you should see it in clear, measurable improvements all across your organization.
By picking the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) from the start, hospital leaders can build a powerful case for the return on investment. This means looking past the technical details and focusing on what really matters: tangible results that affect patients, staff, and the bottom line. The goal is to draw a straight line from seamless data flow to your hospital’s real-world performance.
Key Areas for Measuring ROI
Success isn’t just one number; it’s a story told across three critical areas. Each one gives you a different perspective on how your integration efforts are making a difference.
- Clinical Wins: This is all about patient care. A truly integrated system should make a direct, positive impact on clinical outcomes and patient safety. You can track things like a drop in medication error rates, shorter patient wait times in the ER, or faster turnaround for lab and imaging results. These numbers prove that connected data helps your clinicians make better, faster decisions when it counts.
- Operational Gains: Think efficiency. Integration should be the antidote to the manual workarounds and administrative headaches that waste time and money. Look for metrics like a shorter billing cycle, quicker patient admission times, or a reduction in the hours staff spend on paperwork. These gains don’t just save money; they free up your team to focus on what they do best – caring for patients.
- Financial Health: At the end of the day, the project has to make financial sense. Keep an eye on metrics like a decrease in duplicate lab tests, a higher first-pass claim acceptance rate, and smarter staff allocation based on real-time patient loads. These KPIs translate directly to a healthier bottom line and a more sustainable operation for the long haul.
Tangible Results in Action
The business case becomes impossible to ignore when you see the numbers.
For instance, a regional hospital that tied together its admissions, EHR, and bed management systems was able to cut patient admission times by 30%. That wasn’t just a better patient experience; it optimized bed turnover, which had a direct impact on revenue.
Another great example comes from a multi-clinic network that integrated its clinical and billing platforms. The result? A 25% improvement in billing accuracy. This simple connection drastically cut down on claim denials and sped up their entire cash flow cycle.
These examples, much like the successes highlighted in our client cases, show that a smart integration strategy isn’t an expense; it’s an investment that delivers concrete, valuable results.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hospital System Integration
How long does a hospital integration project take?
The timeline varies significantly based on the project’s scope. A single-system integration, like connecting a new lab system to the EHR, could take 3-6 months. A comprehensive, enterprise-wide integration connecting dozens of systems can take over a year. This is why a phased rollout, focusing on high-impact areas first, is often the most effective strategy.
What are the biggest security risks with integration?
The primary risks involve protecting sensitive patient data. Key concerns are data breaches during transit between systems and unauthorized access to consolidated health records. These are mitigated with a multi-layered security approach, including end-to-end encryption, strict role-based access controls (RBAC), continuous monitoring, and unwavering adherence to HIPAA and GDPR regulations.
Can our old legacy systems be integrated?
Yes, absolutely. Integrating legacy systems is a core function of hospital system integration services. It’s rare for a hospital to have all new technology. Skilled partners use middleware and custom APIs to build secure bridges between older, on-premise systems and modern, cloud-based applications, ensuring they can communicate seamlessly without requiring a complete overhaul of your existing infrastructure.
What’s the difference between HL7 and FHIR?
Think of HL7 (v2) as the traditional, reliable language for exchanging structured data like lab results and patient demographics within a hospital’s internal network. FHIR is the modern, web-based standard designed for the internet age. It uses APIs to make it easier for mobile apps, patient portals, and external systems to securely access and share data in real-time. A robust integration strategy must support both.
At Bridge Global, we don’t just connect systems; we build the secure, intelligent, and scalable bridges that modern healthcare runs on. As your AI solutions partner, our deep experience in custom software development and AI development services can turn your siloed data into a powerful, unified ecosystem.
Discover how to unlock the power of AI for your business and start delivering better outcomes for both your patients and your staff.



